FIGURE 3.
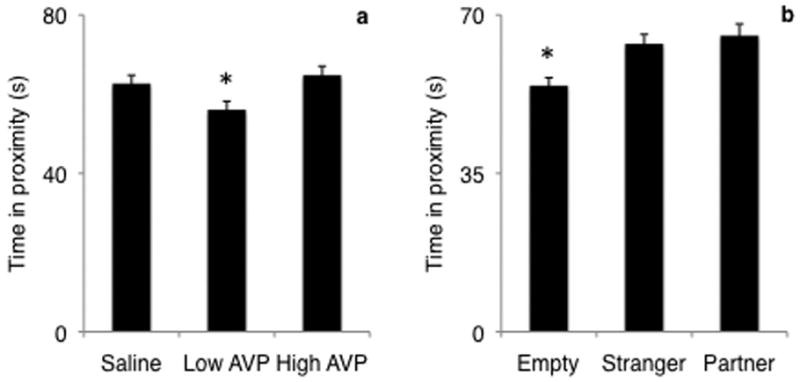
Effect of AVP treatment (a) and stimulus (b) on proximity duration. Male titis were administered varying doses of AVP and the amount of time that they spent in proximity to the stimulus cage was recorded. Both treatment (F2,178=6.74, p=0.0015) and stimulus (F2,178=7.74, p=0.0006) predicted proximity duration. Proximity was greater when low dose AVP was administered, but not when high dose AVP was administered. Proximity was greater when either the partner or the stranger female were presented. Bars represent mean proximity duration ± SEM. * = p < 0.01.
