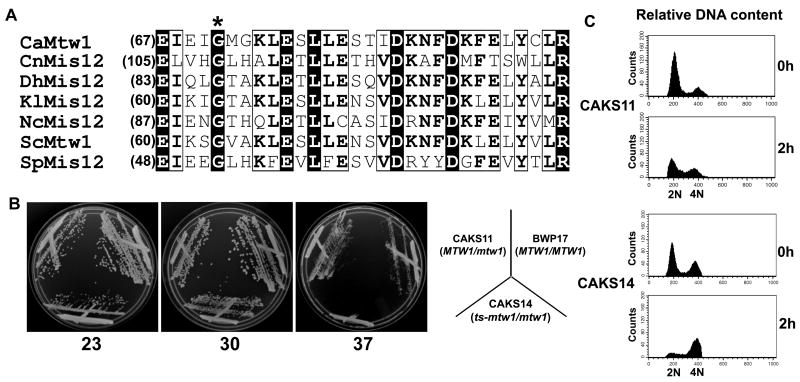
Figure 4.
Mtw1/Mis12 proteins have functional domains that are evolutionarily conserved in C. albicans. (A) Amino acid sequence alignment of two blocks of conserved amino acids present at the N terminal regions of the Mis12/Mtw1 proteins in different organisms: C. albicans CaMtw1, S. cerevisiae ScMtw1, S. pombe SpMis12, N. crassa NcMis12, C. neoformans CnMis12, D. hansenii DhMis12, and K. lactis KlMis12. The conserved glycine residue (asterisk) was mutated to glutamate, resulting in a temperature- sensitive mutation in strain CAKS14 (ts-mtw1/ mtw1). Multiple sequence alignment of the Mis12 sequences was performed by T-Coffee (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/t-coffee) and representation was done by ESPript 2.2 (http://espript.ibcp.fr/ESPript/cgi-bin/ESPript.cgi). (B) CAKS14 cells did not grow at 37°C, yet exhibited robust growth at 23°C and 30°C on YPDU plates for 2 days. Control parent strains BWP17 (MTW1/MTW1) and CAKS11 (MTW1/mtw1) cells grew normally at all three temperatures. (C) Flow cytometry profiles of CAKS11 and CAKS14 cells incubated at 37°C for indicated time points and stained with propidium iodide. The X axis uses propidium iodide staining intensity as a measure of DNA content and the Y axis reports the number of cells.