1.
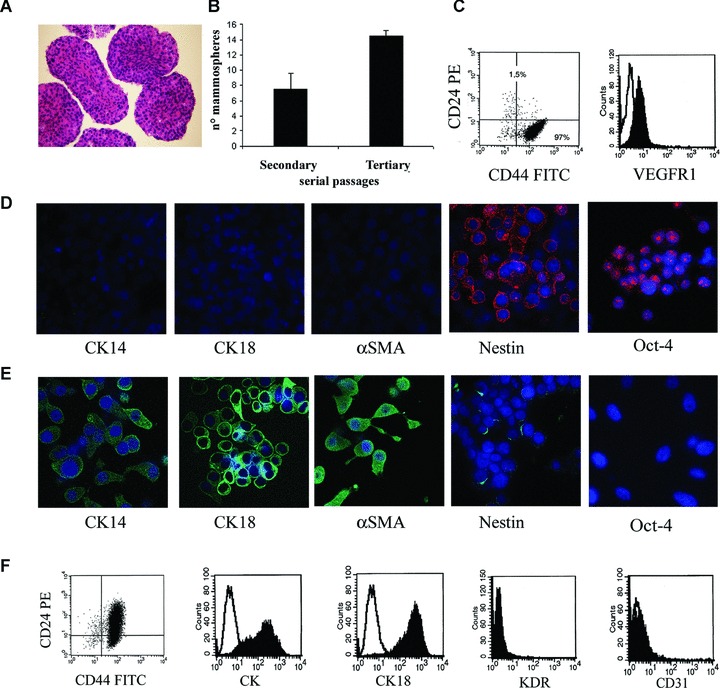
Mammosphere generation, characterization and epithelial differentiation. Mammospheres were obtained by culture of dissociated cells from a human breast tumour in mammosphere medium containing EGF and bFGF. (A) Representative micrograph showing the ematoxilin and eosin staining of paraffin-embedded, formalin-fixed mammospheres. (B) Mammosphere clone formation analysis in secondary and tertiary passages. The number of mammosphere clones/100 cells generated from single cells increased in the third passage. (C) Representative FACS analysis of mammosphere cell clones showing the expression of CD44 and not CD24 and of VEGF receptor 1 (VEGFR1; the dark area indicates the specific Ab, the white area the isotypic control). (D) Representative immunofluorescence expression by mammosphere cell clones of the stem cell markers Oct-4 and nestin, but not of the differentiation markers CK14, CK18 and α-SMA. (E) Serum supplementation and withdrawal of growth factors induced the expression of lineage specific markers of the mature mammary epithelium (CK14, CK18 and α-SMA) in cultured cells from mammosphere clones, with loss of the stem cell markers Oct-4 and nestin. (F) Representative FACS analysis of epithelial differentiated cells showing the acquirement of CD24, the expression of pan-CK and CK18 and the absence of the endothelial cell markers KDR and CD31. The dark area indicates the specific Ab, the white area the isotypic control. Original magnification: panel A: ×100; panel D and E: ×650. Nuclei were counterstained with Hoechst dye.
