Figure 3.
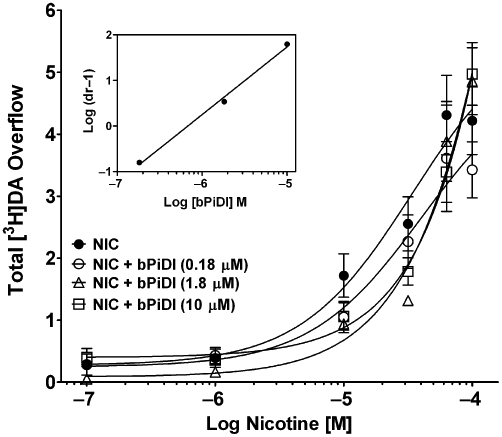
Schild analysis of N,N-decane-1,10-diyl-bis-3-picolinium diiodide (bPiDI) inhibition of nicotine-evoked [3H]dopamine overflow from superfused rat striatal slices. Assay buffer contained nomifensine (10 µM) and pargyline (10 µM) throughout superfusion. After collection of the second sample, slices were superfused with buffer in the absence and presence of bPiDI (0.18, 1.8 or 10 µM) for 36 min before the addition of nicotine (0.1–100 µM) to the buffer, and superfusion was continued for an additional 36 min. For each nicotine concentration, the control response is that for nicotine in the absence of bPiDI. Data are presented as mean ± SEM of total [3H]overflow during the 36-min exposure to nicotine in the absence and presence of bPiDI; n = 4 rats/bPiDI concentration; control, n = 12 rats (bPiDI was between-groups factor, control was contemporaneous with each bPiDI concentration). Concentration–response curves were generated by nonlinear regression. Inset shows the Schild regression in which log (dr–1) was plotted as a function of log [bPiDI] and data were fit by linear regression. DA, dopamine.
