Figure 5.
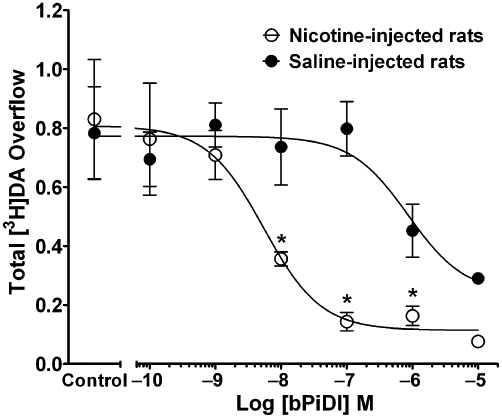
Repeated nicotine treatment increases the potency and inhibitory activity of N,N-decane-1,10-diyl-bis-3-picolinium diiodide (bPiDI). Rats were given nicotine (0.4 mg·kg−1·day−1, s.c., for 10 days) or saline. Twenty-four hours after the last injection, the concentration response for bPiDI (0.1 nM–10 µM) to inhibit nicotine (10 µM)- [3H]dopamine overflow was determined. Slices were superfused with buffer in the absence and presence of bPiDI (0.1–10 µM) for 36 min before the addition of nicotine (10 µM) to the buffer; superfusion continued for 36 min. Control represents [3H]dopamine overflow in response to 10 µM nicotine in the absence of bPiDI. Data are mean ± SEM total [3H]dopamine overflow. n = 6 nicotine-treated rats and n = 7 saline-treated rats. Concentration-response curves were generated by nonlinear regression. * Indicates significant difference between repeated nicotine and repeated saline control groups (P < 0.05). DA, dopamine.
