Figure 6.
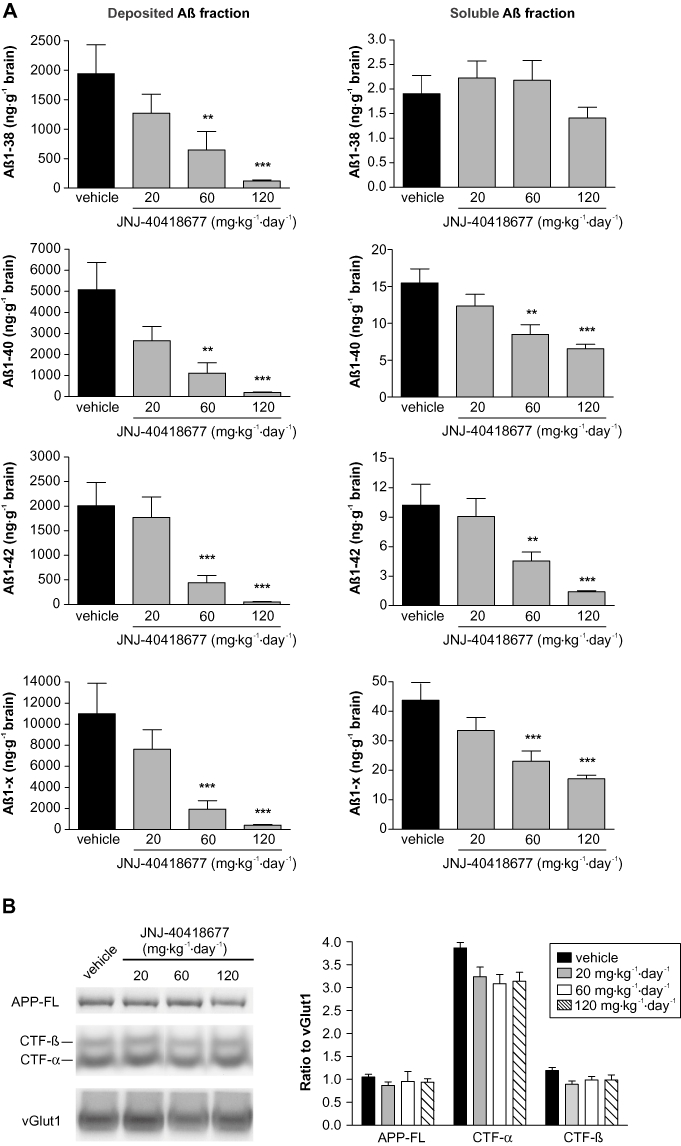
(A) Brain Aβ levels were reduced after chronic treatment of Tg2576 mice with JNJ-40418677 via a medicated diet. Female Tg2576 mice were treated from 6 to 13 months of age with 20 (n = 16), 60 (n = 13) or 120 mg·kg−1·day−1 (n = 16) JNJ-40418677 or vehicle (n = 15). Mean (+SEM) levels of human Aβ1–x, Aβ1–38, Aβ1–40 and Aβ1–42 in deposited (left histograms) and soluble (right histograms) brain fractions were measured by differential elisas and expressed as ng·g−1 brain. Chronic administration of JNJ-40418677 resulted in dose-dependent reductions of all Aβ species measured in soluble and deposited fractions, except for soluble Aβ1–38. (B) No changes in the steady state levels of full-length APP (APP-FL), CTF-α and CTF-β were observed after chronic treatment of Tg2576 mice with JNJ-40418677 via a medicated diet up to 120 mg·kg−1·day−1. Representative Western blots of membrane fractions of brains of Tg2576 mice treated with vehicle and various doses of JNJ-40418677 are shown. Antibodies JRF/Abtot/17 and C1/6.1 were utilized for detection of APP-FL and APP-CTF respectively. Data from densitometric analyses are expressed as ratio of APP-FL, CTF-α and CTF-β signals to loading control vGlut1. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus vehicle.
