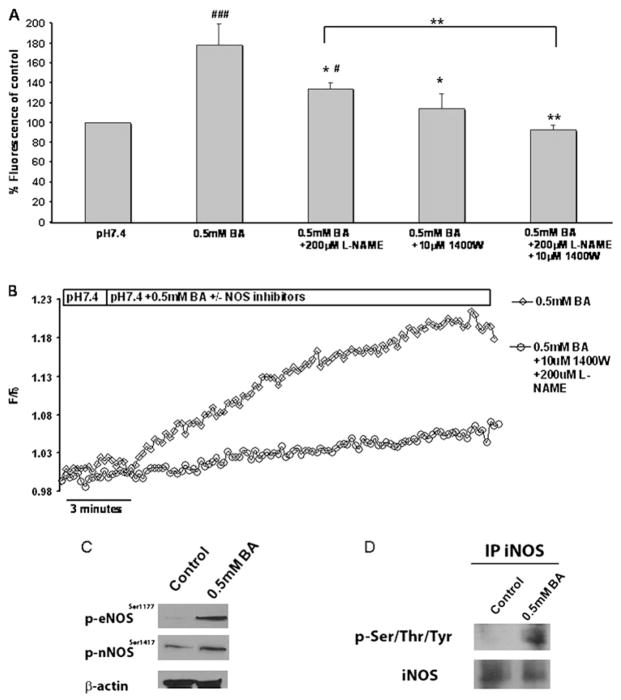
Figure 2.
Increased nitric oxide (NO) production and nitric oxide synthase (NOS) activation is induced by bile acid cocktail (BA). CP-A cells were exposed to 0.5 mM BA in the presence or absence of the NOS inhibitors NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME) and 1400W. (A) Relative DAF-FM fluorescence after 1 min treatments at excitation/emission wavelengths 490/535 nm. The results represent mean±SEM from at least three independent experiments. (*p<0.05, **p<0.01 compared to pH 5.5 +0.5 mM BA), (#p<0.05 ###p<0.001 compared to pH 7.4). (B) Representative real-time traces of DAF-FM fluorescence. (C) Western blots of phosphorylated eNOS and nNOS and β-actin in CP-A cells +/− 0.5 mM BA for 5 min. (D) The presence of phosphorylated iNOS in CP-A cells treated with 0.5 mM BA detected by immunoprecipitation with iNOS antibody and blotting with iNOS or phospho-Ser/Thr/Tyr antibody.