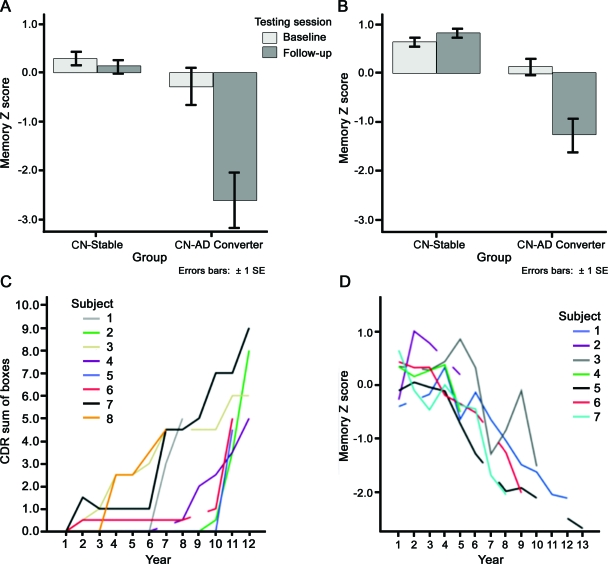
Figure 1. Baseline and longitudinal clinical characteristics of the 2 samples.
(A, B) Baseline and follow-up episodic memory Z scores from the 2 samples, illustrating the stability (or even slight improvement in sample 2) of performance in the cognitively normal (CN)-stable groups over nearly a decade of follow-up. In contrast, the CN-Alzheimer disease (AD) converters performed normally at baseline but declined substantially over nearly a decade of follow-up by the time of diagnosis of AD dementia. (C, D) Detailed illustration of cognitive decline in each of the CN-AD converter individuals. (C) Annual Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR)–sum of boxes scores increased from normal (0) at baseline to mild dementia in each of the 8 individuals in the Massachusetts General Hospital sample. (D) Annual episodic memory Z scores declined from normal to substantially impaired in each of the 7 individuals in the Rush sample. Breaks in lines indicate years for which data were not available.