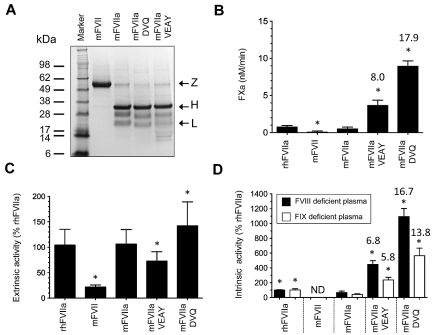
Figure 2.
Characterization of recombinant proteins. (A) Approximately 4 μg of purified protein (mFVII, mFVIIa, mFVIIa-DVQ and mFVIIa-VEAY) was electrophoresed under reducing conditions and stained with Coomassie blue. The molecular sizes of the marker are shown on the left. Arrows indicate the zymogen form (Z), heavy (H) and light (L) chains. The lower-molecular-weight bands (10-16 kDa) are most likely degradation products, as have been previously observed in human recombinant FVIIa preparations.32,33 The differential staining of light and heavy chains with Coomassie blue is commonly found in human32,33 as well as murine FVIIa preparations.10,14 (B) Proteolytic activity of proteins using human FX as a macromolecular substrate in the absence of tissue factor expressed as nM FXa/min. Data were derived from at least 3 independent experiments. *P < .04 compared with mFVIIa. Fold increase is indicated relative to mFVIIa. (C) Extrinsic coagulant activity of recombinant proteins (% of rhFVIIa) in human FVII–deficient plasma. (D) Intrinsic coagulant activity of recombinant proteins (% of rhFVIIa) in human FVIII or FIX deficient plasma. Data for panels C and D were derived from at least 4 experimental points. *P < .03 compared with mFVIIa. ND indicates not detectable. Fold increase in activity in panels C and D is indicated relative to mFVIIa. All data are shown as average ± 1 SD.