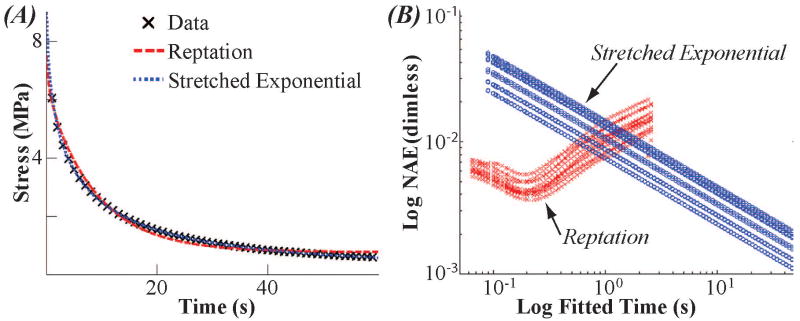
Figure 2.
Polymer dynamics models describe short-term cartilage stress-relaxation. The monodisperse reptation model (red) fit the initial (∼0-0.1 s) stress-relaxation best while the stretched exponential model (blue) fit increasingly well with increasing relaxation time. (A) A representative fit of both the monodisperse reptation and stretched exponential models. (Compressive stress presented as positive for illustration purposes.) (B) Normalized Average Error versus Fit Time for 60 second data. The monodisperse reptation model (red X's) shows a minimum error. The stretched exponential model (blue circles) fits better as more data is fit. For time less than one second, the fit to the monodisperse reptation model has smaller error than the stretched exponential.