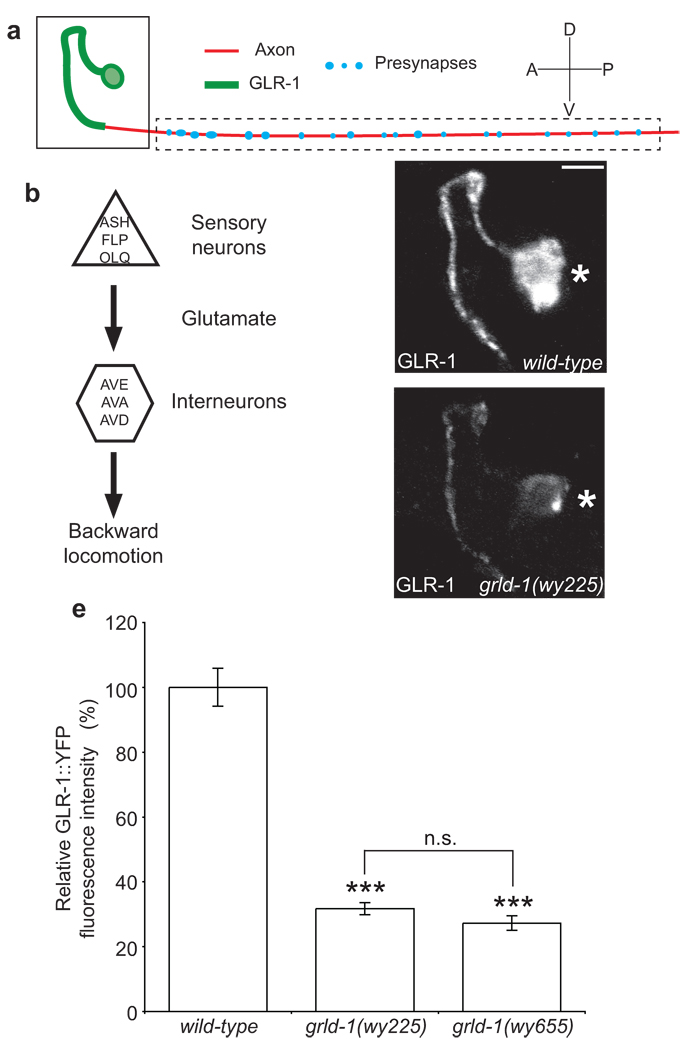
Figure 1. grld-1(wy225) mutants have decreased levels of GLR-1 in AVE.
(a) Schematic diagram of AVE: green represents postsynaptic segment; red denotes axonal segment of the AVE process. (b) Circuit diagram of the nose-touch avoidance response. The sensory neurons ASH, FLP, and OLQ release glutamate to their glr-1-expressing synaptic partners, the interneurons AVE, AVA, and AVD. AVE, AVA, and AVD synapse onto the A-type motor neurons that stimulate the body wall muscles resulting in backwards locomotion. (c, d) Representative confocal image of GLR-1::YFP fluorescence in AVE of L2-stage wild-type (c) and grld-1(wy225) animals (d). The same region as boxed in a is shown. Asterisk, AVE cell body. Scale bar, 2 µm. (e) Comparison of GLR-1::YFP fluorescence intensity (normalized to wild-type) between wild-type, grld-1(wy225), and grld-1(wy655) worms. n > 20. Error bars, s.e.m. ***P < 0.001, n.s. = not significant, compared to wild-type animals unless otherwise depicted, t-test.