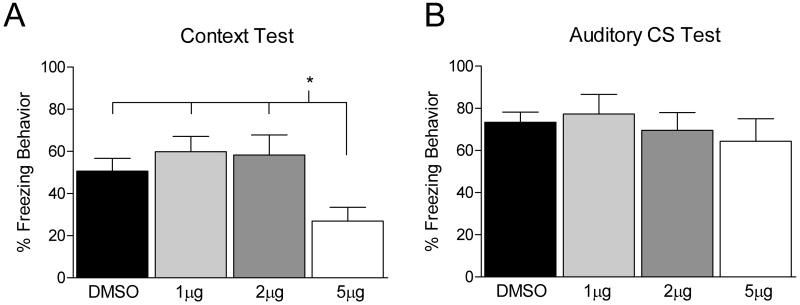
Figure 3.
Bars represent mean percentage freezing behavior (±SEM). Rats were trained with 4 white noise – shock pairings (data not shown). Immediately after training animals received an infusion of DMSO vehicle or 1, 2 or 5 μg/μl RAP into the DH. Animals that received DMSO (black bar) or RAP (1μg/μl, light gray bar; 2μg/μl, dark gray bar; 5μg/μl, white bar) were tested 24 hours later to the training context (A) as well as to the white noise in a novel context (B). The group that received 5μg/μl of RAP showed significantly disrupted freezing to the context 24 hours later. No differences in freezing behavior were found during exposure to the white noise cue.