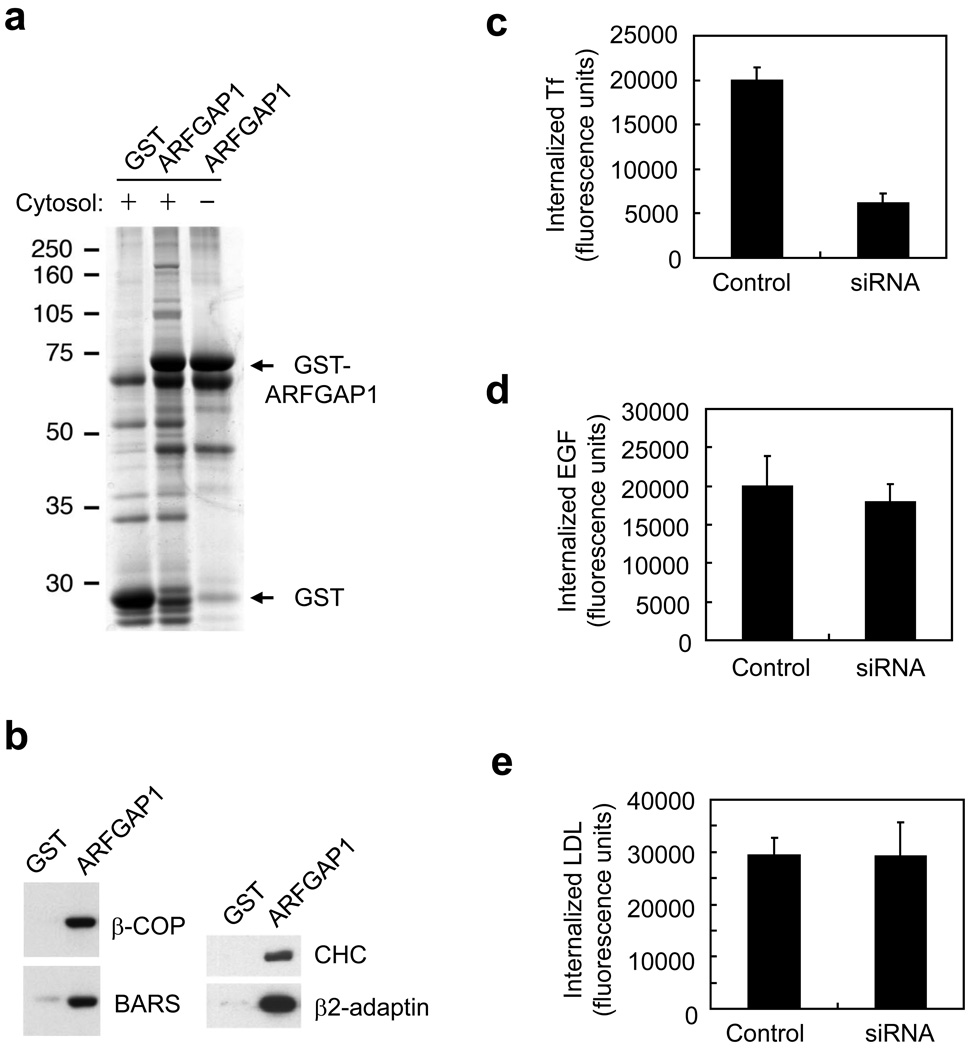
Figure 1. Interactions with ARFGAP1 and effects of its knockdown.
a. Pull-down assay detects proteins interacting with ARFGAP1. ARFGAP1 as a GST fusion protein was bound to glutathione beads, incubated with cytosol, and then analyzed for associated proteins by Coomassie staining.
b. Pull-down assay detects ARFGAP1 interacting with coat components. ARFGAP1 as a GST fusion protein was bound to glutathione beads, incubated with cytosol, and then immunoblotted for proteins as indicated. ARFGAP1 interacts with components of AP-2, and also with previously known interacting proteins that are components of the COPI complex.
c. Tf uptake is reduced by siRNA against ARFGAP1. BSC-1 cells were bound with fluorescence-conjugated Tf, and then assessed for the level of internalized Tf at 10 minutes. The mean from three experiments with standard error is shown. Difference between the two conditions is significant (p<0.05).
d. EGF uptake is not markedly affected by siRNA against ARFGAP1. BSC-1 cells were with fluorescence-conjugated EGF, and then assessed for the level of internalized EGF at 10 minutes. The mean from three experiments with standard error is shown. Difference between the two conditions is insignificant (p>0.05).
e. LDL uptake is not markedly affected by siRNA against ARFGAP1. BSC-1 cells were bound with fluorescence-conjugated LDL, and then assessed for the level of internalized LDL at 10 minutes. The mean from three experiments with standard error is shown. Difference between the two conditions is insignificant (p>0.05).