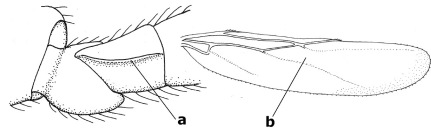
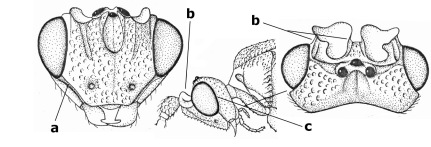
| 1. | Fore tarsal claws bifurcate, the inner tooth usually large and with no lobe (a); outer face of middle tibia without submedial pegs (b), but with one peg in Coronagathis; area between antennal sockets with a pair of crests or carinae (c), less frequently (about 30 %) with a trough (cc) or tubercle | 2 |
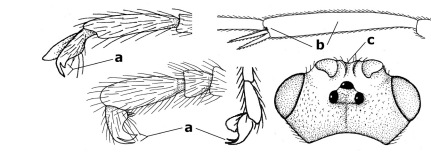 |
||
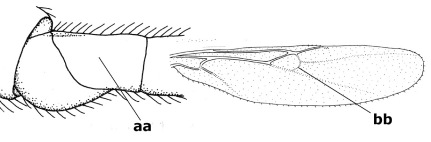
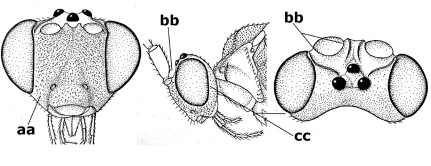
| – | Fore tarsal claws simple or with a more or less lamelliform, basal lobe (aa); outer face of middle tibia with pegs submedially or pegs in a subapical cluster (bb); area between antennal sockets usually with a simple median elevation or with a trough (cc) | 13 |
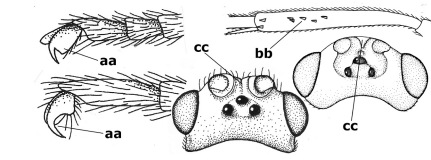 |
||
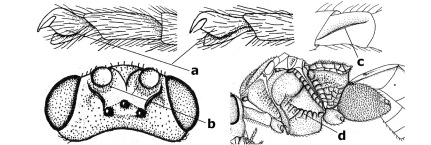
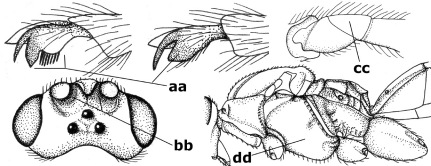
| 2. | Notauli completely absent and area smooth (a); gena more or less protruding postero-ventrally (b); inner tooth of bifurcate fore claws larger than its outer tooth (female) or teeth equal (male) (c) | 3 |
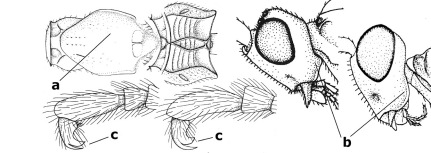 |
||
| – | Notauli at least in anterior half of mesoscutum impressed (aa), if shallowly impressed then area distinctly sculptured; gena variable postero-ventrally (bb); inner tooth of bifurcate fore claws as large as its outer tooth or smaller (both sexes; cc) | 4 |
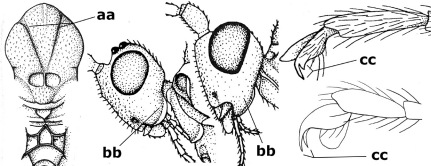 |
||
| 3. | Outer ventral margin of hind trochantellus with a carina (a) and basally angulate; ovipositor sheath short, about as long as apical height of metasoma; vein 2r-m of hind wing absent (b); [scutellum with subposterior elevation (but sometimes reduced); epomial carinae double or single; semi-circular crest present behind antennal sockets; vein SR1 of fore wing rather curved] | Gyrochus Enderlein, 1920 |
 |
||
| – | Outer ventral margin of hind trochantellus without carina (aa) and not or only slightly angulate basally; ovipositor sheath long, about as long as fore wing or somewhat shorter; vein 2r-m of hind wing indicated (bb) | Biroia Szépligeti, 1900 |
 |
||
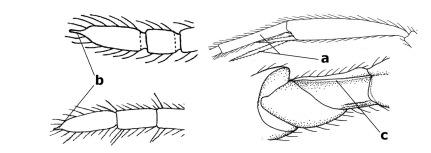
| 4. | Inner spur of middle tibia 0.8–1.1 times as long as middle basitarsus (a); apex of antenna with short to medium-sized spine (b), sometimes minute; ovipositor sheath short, about as long as apical height of metasoma, hardly or not protruding; hind trochantellus usually with a distinct ventral carina on its outer edge (c) or edge distinctly angulate; [apex of the ovipositor sheath blunt apically and with numerous ampulliform papillae]; Coccygidium complex | 5 |
 |
||
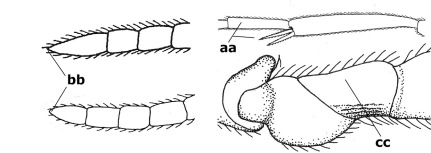
| – | Inner spur of middle tibia 0.4–0.7 times as long as middle basitarsus (aa); apex of antenna without spine (bb); relative length of ovipositor sheath vari able; ventral carina of hind trochantellus often (about two-thirds) absent or obsolescent (cc) | 7 |
 |
||
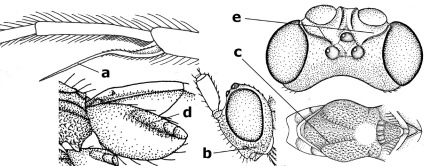
| 5. | Malar suture long and deep (a); outer and inner side of antennal socket strongly protruding (b); eye with distinct subocular groove posteriorly (c); [hind coxa much longer than first tergite; not yet found but may occur in South Vietnam] | Hypsostypos Baltazar, 1963 |
 |
||
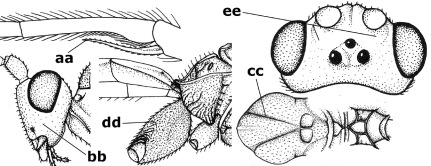
| – | Malar suture absent (aa); outer side of antennal socket weakly protruding (bb), eye without subocular groove posteriorly (cc) | 6 |
 |
||
| 6. | Fore tibial spur with a long curved and glabrous apical spine (a); malar space rugulose (b); notauli comparatively wide (c); hind coxa with longitudinal carina or rugae (d); frons with lateral crests or carinae more or less developed (e) | Coccygidium de Saussure, 1892 |
 |
||
| – | Fore tibial spur with a short, straight and setose apex (aa); malar space smooth or punctate (bb); notauli comparatively narrow (cc); hind coxa without longitudinal carina or rugae (dd); frons without lateral crests or carinae (ee); [area between antennal sockets without a pair of carinae; temples medium-sized; ventral surface of hind femur densely rugose] | Zelodia gen. n. |
 |
||
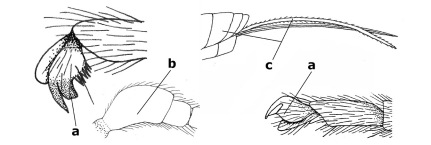
| 7. | Inner or outer hind claw with a distinct wide and acute lobe submedially or a wide dark obtuse submedial lamella (a); if rather narrow then about as long as apical tooth; outer aspect of scapus partly smooth and somewhat concave (b); ovipositor sheath slender and much longer than apical height of metasoma (c); [frons without a pair of lamellae between antennal sockets] | 8 |
 |
||
| – | Inner and outer hind claw bifurcate, with a small subapical inner tooth or (nearly) simple (aa); if with a rather flattened inner tooth then this distinctly shorter than apical tooth; outer aspect of scapus punctate or punctulate and usually less concave (bb); ovipositor sheath more or less widened and short, about as long as apical height of metasoma or less (cc) | 9 |
 |
||
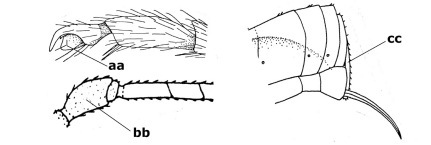
| 8. | Outer hind tarsal claw with a distinct lobe similar to lobe of inner hind tarsal claw and no pecten (a); area near inner side of antennal sockets shallowly depressed (b); mesosternal sulcus deep and coarsely crenulate; hind trochantellus more or less carinate ventrally (c; but may be rounded or nearly so); at least posterior half of precoxal sulcus distinctly crenulate (d); [not yet found but likely to occur in North Vietnam] | Cremnoptoides van Achterberg & Chen, 2004 |
 |
||
| – | Outer hind tarsal claw with a dentiform or squarish black lamella and more or less with a black pecten basally and different from lobed inner claw (aa); area near inner side of antennal sockets deeply depressed (bb); mesosternal sulcus shallow and smooth or nearly so; hind trochantellus rounded ventrally (cc); precoxal sulcus absent or nearly so (dd) | Cremnops Foerster, 1862 |
 |
||
| 9. | Scutellum with a pair of large horns and axillae protruding (a); subbasal cell of hind wing narrower than plical lobe (b); hind coxa long, exceeding length of first tergite and coarsely sculptured (c) | Coronagathis gen. n. |
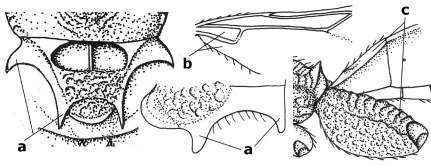 |
||
| – | Scutellum without a pair of tubercles (aa); subbasal cell of hind wing about as wide as plical lobe (bb); hind coxa shorter, at most as long as first tergite (cc), if rarely somewhat longer than coxa largely smooth | 10 |
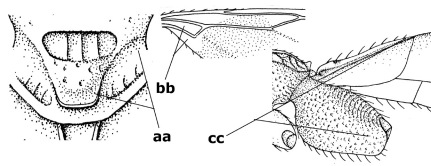 |
||
| 10. | Frons without lateral carinae (a); vein M+CU of hind wing at most 0.8 times vein 1-M (b); labio-maxillary complex only slightly protruding (c) | Euagathis Szépligeti, 1900 |
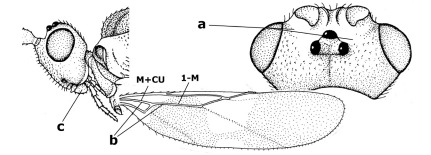 |
||
| – | Frons with lateral carinae (aa); vein M+CU of hind wing longer than vein 1-M or subequal (up to 0.9 times; bb); labio-maxillary complex usually rather protruding (cc, but not in Oreba) | 11 |
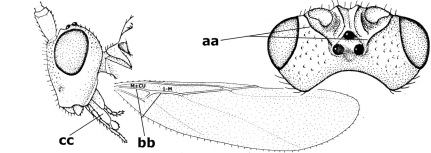 |
||
| 11. | First subdiscal cell of fore wing distinctly higher than first discal cell (a); body metallic; marginal cell of hind wing ends in front of wing apex (b); vein m-cu of fore wing subparallel to vein 1-M (c); area between antennal sockets with an obtuse tubercle (d); [outer ventral margin of hind trochantellus cariniform; only the North Oriental type species (Oreba purpurea Cameron, 1900) is known; not yet found in Vietnam but may occur in the northern mountains] | Oreba Cameron, 1900 |
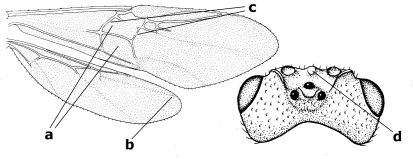 |
||
| – | First subdiscal cell of fore wing lower than first discal cell (aa; Disophrys) or subequal (aaa; Troticus); body non-metallic; marginal cell of hind wing close to wing apex (bb); vein m-cu of fore wing diverging from vein 1-M (c); area between antennal sockets with a pair of carinae or crests (dd) | 12 |
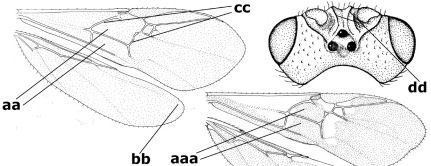 |
||
| 12. | Prepectal carina distinctly angulate subdorsally (a); lateral carina of frons pointing to anterior ocellus or between anterior and posterior ocelli (b); scapus robust compared to third antennal segment and straight (c); [hind trochantellus rounded ventrally] | Troticus Brullé, 1846 |
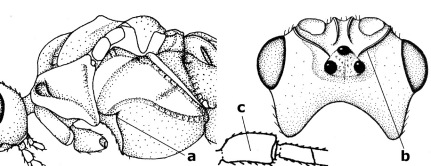 |
||
| – | Prepectal carina evenly curved subdorsally (aa); lateral carina of frons pointing to posterior ocellus (bb); scapus less robust compared to third antennal segment and more or less bent (cc) | Disophrys Foerster, 1862 |
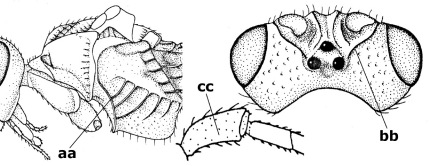 |
||
| 13. | Veins of fore wing largely absent (a); hind trochantellus much longer than trochanter (b); hind tibia with blackish bristles (c); pedicellus enlarged (d); [not yet found in Vietnam, but expected to occur] | Aneurobracon Brues, 1930 |
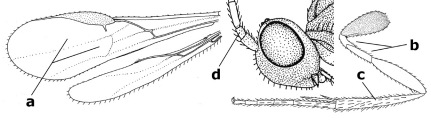 |
||
| – | Veins of fore wing largely present (aa); hind trochantellus about as long as trochanter or shorter (bb); hind tibia without black bristles (cc); pedicellus short (dd) | 14 |
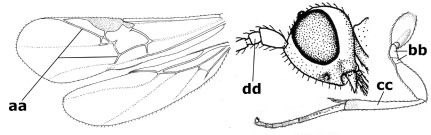 |
||
| 14. | Vertical axis [v] of malar triangle 1.7–6.0 times its horizontal axis [h] and the part of head below eyes only gradually narrowed ventrally (a) to parallel-sided; clypeus strongly convex (b); mouth-parts more or less lengthened in form of a beak, galea nearly always distinctly longer than 1.3 times its width, longer than labial palp (c); [mainly Holarctic, but some species reach the northern Oriental region] | Agathis Latreille, 1804 |
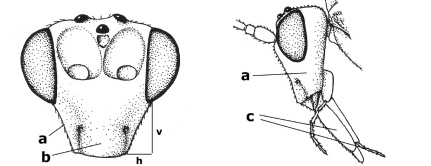 |
||
| – | Vertical axis [v] of malar triangle 1.0–1.5 times its horizontal axis [h] and the part of head below eyes directly narrowed ventrally (aa); clypeus usually at least partly flattened (bb), only in Therophilus mediator-group distinctly convex (bbb); mouth-parts normal, galea not longer than wide, shorter than labial palp and usually hardly or not visible in lateral view (cc) | 15 |
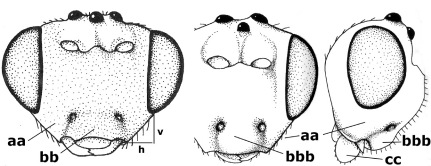 |
||
| 15. | Fore and middle tarsal claws simple and comparatively robust (a); area behind antennal sockets deeply impressed (b); [vein 1-M of hind wing 1.1–1.6 times as long as vein M+CU] | Bassus Fabricius, 1804 s.s. |
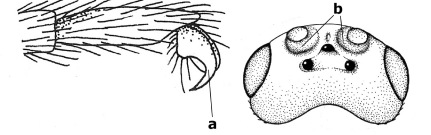 |
||
| – | Fore and middle tarsal claws nearly always with a distinct basal lobe and comparatively slender (aa); area behind antennal sockets nearly always moderately to shallowly impressed (bb); [vein 1-M of hind wing 0.6–1.4 times as long as vein M+CU] | 16 |
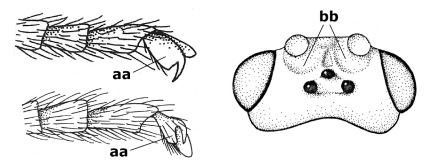 |
||
| 16. | Vein 1-SR+M of fore wing more or less developed (a), usually sclerotised medially, but sometimes only as a brownish pigmented stripe and notauli absent (but mesoscutum medio-posteriorly with a deep to superficial depression; b) | Earinus Wesmael, 1837 |
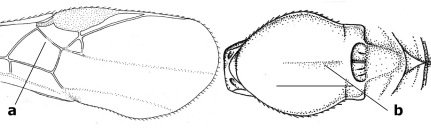 |
||
| – | Vein 1-SR+M of fore wing medially absent, not sclerotised and usually without pigmentation (aa), if pigmented then notauli complete (bb) | 17 |
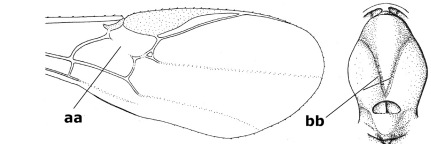 |
||
| 17. | Antennal sockets with a circular carina reaching dorsally as high as level of anterior ocellus (a); temples with a lateral tubercle (b); genal protuberance present and protruding ventrally (c); scutellum with a distinct subposterior crest (d) and medio-posterior depression transverse (e); [transverse metasternal carina non-lamelliform and beyond upper level of hind coxal cavities] | Gyragathis gen. n. |
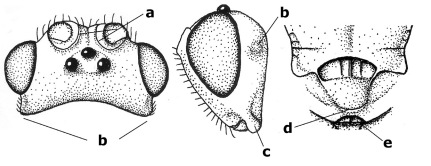 |
||
| – | Antennal sockets without a circular carina (aa); temples without a lateral tubercle (bb); protuberance absent (cc), if present then protruding posteriorly; scutellum without a distinct subposterior crest (dd) and transverse medio-posterior depression absent, obsolescent or semicircular (ee) | 18 |
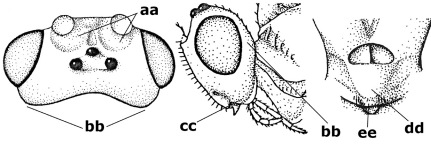 |
||
| 18. | Outer side of antennal sockets distinctly lamelliform protruding in dorsal view (a); subpronope deep, wide and epomia strongly developed (b); basal half of third metasomal tergite usually with sharp lateral margin (c); dorsal carinae of first tergite usually long and costate (d); propodeal spiracle comparatively large and elliptical (e); ramellus of fore wing usually present (f); [transverse metasternal carina lamelliform; no subposterior crest of scutellum] | Braunsia Kriechbaumer, 1894 |
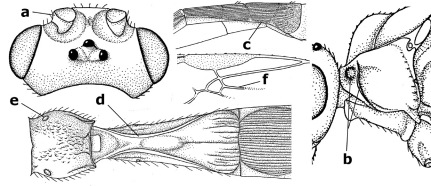 |
||
| – | Outer side of antennal sockets not or only slightly protruding in dorsal view (aa), sometimes as a narrow lamella; subpronope comparatively shallow and epomia medium-sized to weakly developed (bb); basal half of third tergite often without sharp lateral margin or weakly developed (cc), except in Lytopylus; dorsal carinae of first tergite usually weakly developed (dd) or absent; propodeal spiracle medium-sized to small, round or sub-elliptical (ee); ramellus of fore wing absent (ff) | 19 |
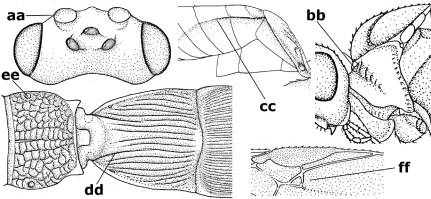 |
||
| 19. | Vein r-m of fore wing absent (a); first metasomal tergite and often also metapleuron granulate and dull and tergite distinctly convex medially and dorsal carinae absent (b); precoxal sulcus about 0.6 times as long as mesopleuron and sculptured (c) or superficially impressed and smooth | Camptothlipsis Enderlein, 1920 |
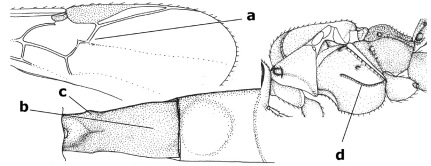 |
||
| – | Vein r-m of fore wing present (aa), rarely obsolescent; sculpture of first tergite and metapleuron variable (bb), if granulate then first tergite less convex medially and with dorsal carinae (bbb); precoxal sulcus longer than 0.6 times length of mesopleuron and sculptured (cc) or absent | 20 |
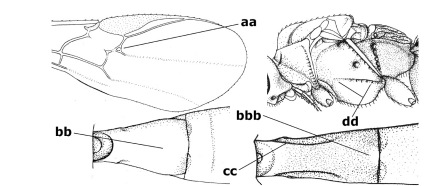 |
||
| 20. | First metasomal tergite 5–6 times as long as wide apically (a) and 1.6–1.7 times as long as hind coxa (b); frons flattened anteriorly except for a short median depression (c); hind femur short compared to hind coxa (d); hind basitarsus with numerous spiny setae ventrally (e); [not yet found in Vietnam but expected to occur; synonymised with Lytopylus Foerster by Sharkey et al. (2009), but it runs in their key to Therophilus Wesmael. Provisionally retained as separate genus because of the synapomorphous character states (a-d) listed above] | Facilagathis van Achterberg & Chen, 2004 |
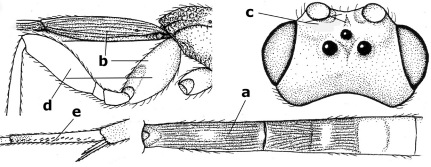 |
||
| – | First tergite 1–3 times as long as wide apically (aa) and about as long as hind coxa (bb); frons partly convex anteriorly and behind antennal sockets concave (cc); hind femur longer compared to hind coxa (dd); hind basitarsus only bristly setae ventrally (ee) | 21 |
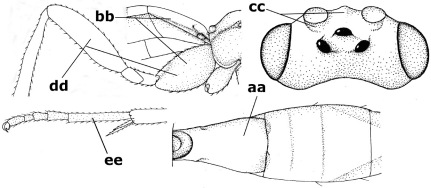 |
||
| 21. | Metasomal cavity [mc] at most reaching upper level of hind coxal cavities [hcc] (a); transverse metasternal carina [tmc] (= carina behind metasomal cavity) straight or nearly so and coarsely developed (b); anterior half of third metasomal tergite often more or less coarsely striate (c), but sometimes smooth | Lytopylus Foerster, 1862 |
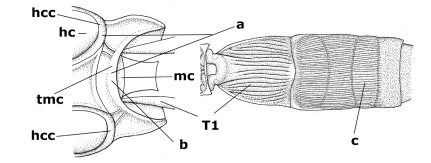 |
||
| – | Metasomal cavity [mc] protruding beyond upper level of hind coxal cavities [hcc] (aa); transverse metasternal carina [tmc] curved and less developed (bb); sculpture of anterior half of third tergite variable, usually smooth or finely striate (cc) | Therophilus Wesmael, 1837 |
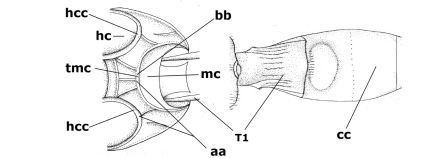 |

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.