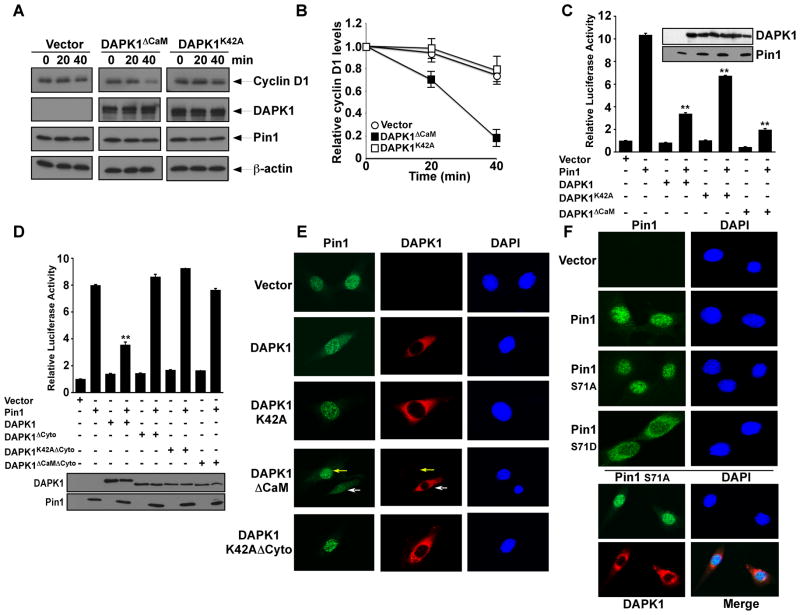
Figure 4. DAPK1 inhibits Pin1 nuclear localization and cellular function.
(A and B) DAPK1 inhibits the ability of Pin1 to stabilize cyclin D1 protein. Pin1−/− MEFs expressing Pin1 and DAPK1ΔCaM, DAPK1K42A or vector control were treated with cycloheximide, followed by immunoblot analysis (A) and semi-quantitated using β-actin (B). Results shown are mean ± SEM, n = 3.
(C) DAPK1 inhibits the ability of Pin1 to activate cyclin D1 promoter in cells. HeLa cells were transiently transfected with Pin1, reporter constructs and DAPK1, its mutants or vector control, followed by assaying the luciferase activity. Results shown are mean ± SEM, n = 3. **, p <0.01.
(D) DAPK1 and Pin1 binding is required for DAPK1 to inhibit Pin1-mediated cyclin D1 activation. Results shown are mean ± SEM, n = 3. **, p <0.01.
(E) DAPK1 prevents Pin1 nuclear localization. Cells expressing DAPK1, its mutants or control were immunostained with anti-Pin1 (green), anti-DAPK1 (red) antibodies and DAPI (blue). White and yellow arrows point to DAPK1ΔCaM-transfected and non-transfected cells, respectively.
(F) Ser71 phosphorylation regulates Pin1 localization. Cells inducibly expressing Pin1 or its Ser71 mutants or inducibly expressing DAPK1 with Pin1S71A overexpression were stained with anti-HA (green) or FLAG (red) antibodies and DAPI (blue).