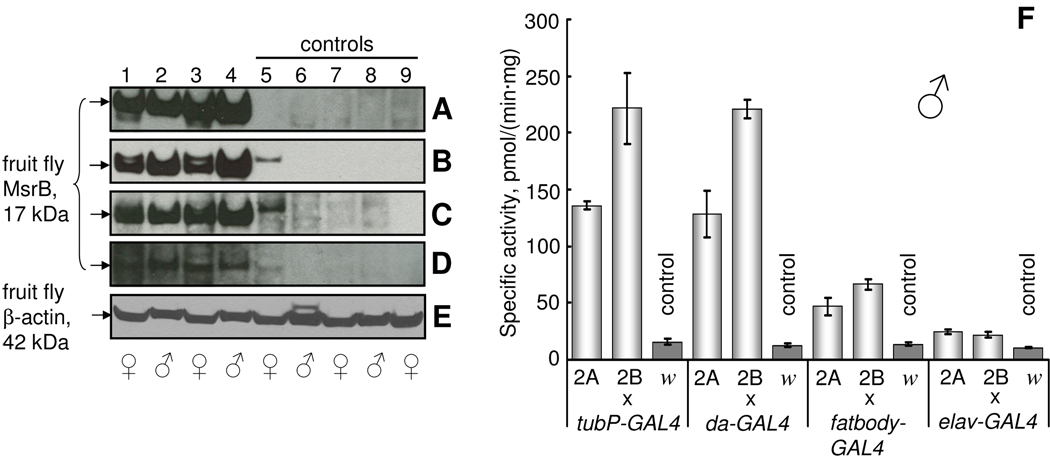
Fig. 2.
Expression of Drosophila MsrB in fruit flies. (A–D) Western blot analyses of fruit fly total homogenates with anti-Drosophila MsrB antibodies. dMsrB2A (lanes 1, 2) and dMsrB2B (lanes 3, 4) flies were crossed to GAL4-activator lines to overexpress Drosophila MsrB. Controls were obtained by crossing white flies with dMsrB2A (lanes 5, 6), dMsrB2B (lanes 7, 8) and GAL4-activator (lane 9) lines. F1 progeny of crosses between tubP-GAL4 (A), da-GAL4 (B), fatbody-GAL4 and elav-GAL4 (D) drivers and dMsrB (lanes 1–4) and white flies w1118 (lane 9) were analyzed. Adult animals used were 6 days old. Migration of the 17 kDa band corresponding to fruit fly MsrB is shown by arrows on the left in panels A–D. (E) Protein loading control (42 kDa Drosophila β-actin) for the Western blotting experiment presented in A. Gender of 6-day-old females and males analyzed is shown by the corresponding symbols below panel E. (F) MsrB activity of total homogenate of fruit flies used for Western blot analyses. Designations 2A, 2B and letter w refer to mMsrB23A, mMsrB22A and w1118 lines that were crossed with the indicated GAL4-driver. Measurements were performed in triplicate. All data are reported as the means ±S.D.