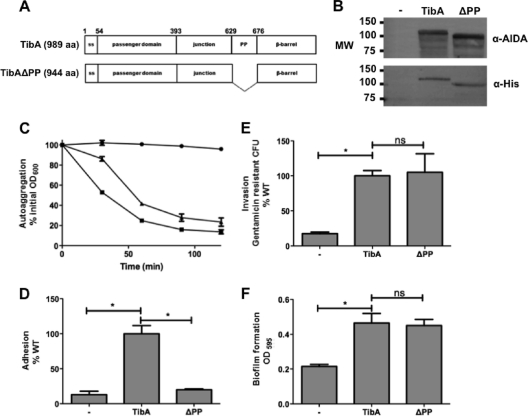
Fig. 5.
Construction and expression of TibA lacking the proline-rich region. (A) Schematic representation of TibA and the proline-rich region deletion mutant TibAΔPP. (B) Whole-cell lysates of bacteria bearing an empty vector (−), a plasmid allowing the expression of His-TibA, or the proline-rich region deletion mutant (ΔPP) were probed with an antibody raised against glycosylated AIDA-I (top) or against the His tag (bottom). MW, molecular weight (in thousands). (C to F) Autoaggregation (C), adhesion (D), invasion (E), and biofilm formation (F) assays were performed, as described in the legend of Fig. 3, on bacteria bearing an empty vector (− [•]) or plasmids allowing the expression of TibA (WT [▪]) or TibA deleted for the proline-rich region (ΔPP [▴]). ANOVA and Dunnett posttests were used to identify significant differences (* [P < 0.05]) and nonsignificant differences (ns).