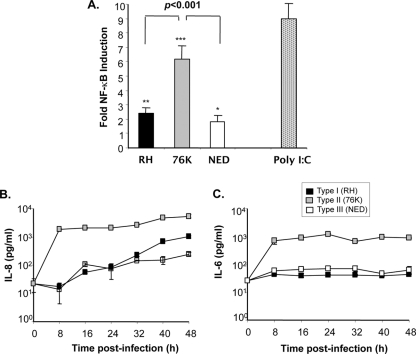
Fig. 2.
Type I and type III T. gondii strains induce low levels of NF-κB activation and poor cytokine secretion in human IEC compared to type I parasites. (A) NF-κB activation. IEC were infected by each T. gondii genotype strain at a MOI of 5 or stimulated with the TLR3 ligand [poly(I:C); 50 μg/ml]. NF-κB activation was measured by a reporter gene assay at 24 h postinfection. Results were expressed as fold NF-κB inductions obtained after the number of relative light units for infected cells was normalized to that for noninfected cells. ***, P < 0.0001; **, P < 0.001; *, P < 0.05. Data are representative of three experiments, performed in triplicate at each time point (B and C) Differential induction of IL-8 and IL-6 secretion by the three T. gondii genotypes strains. Cells were cultured in 24-well plates (3 × 105 cells/well) and infected with the three T. gondii genotypes at a MOI of 1. Cytokine secretion in culture supernatants from infected cell cultures collected at 8-h intervals for a period of 48 h was measured by a sandwich ELISA. Optical densities obtained were converted to cytokine concentrations using standard curves of known concentration for each cytokine. Data are representative of three experiments performed in triplicate at each time point.