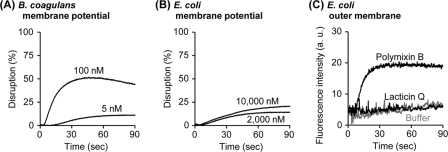
Fig. 2.
Disruption of membrane potential and outer membrane permeabilization by lacticin Q. (A and B) Washed cells of B. coagulans (A) or E. coli (B) and DiSC3(5) were diluted using buffer M (250 mM sucrose, 5 mM MgSO4, 10 mM potassium phosphate, pH 7.0) in a 2-ml quartz cuvette incubated at 30°C [optical density of cells at 600 nm (OD600) = 0.05, 1 μM DiSC3(5)]. The excitation (EX) and emission (EM) wavelengths were set at 622 and 675 nm, respectively. At the beginning of the measurement, lacticin Q was added at the indicated concentrations. As controls, 0% leakage and 100% leakage were obtained by the addition of buffer and 0.1% Triton X-100, respectively. (C) The peptide-induced E. coli outer membrane permeabilization was determined with the NPN uptake assay. Washed cells of E. coli and NPN were diluted using buffer N (5 mM HEPES-NaOH, 5 mM glucose, 100 mM NaCl, 5 μM carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone, pH 7.4) in a 2-ml quartz cuvette (OD600 = 0.5, 10 μM NPN). The EX and EM wavelengths were set at 350 and 420 nm, respectively. At the beginning of the measurement, 10 μM lacticin Q was added. The outer membrane-permeabilizing antibiotic polymyxin B (1 mg/ml) and the buffer N were applied for the positive and negative controls, respectively. a.u., arbitrary units.