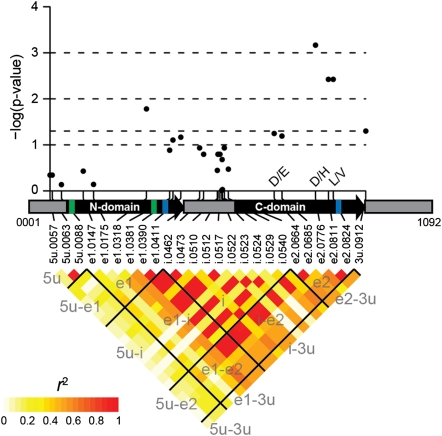
Fig. 2.
Multivariate associations and LD in the GST gene. The gene structure is portrayed as gray boxes for the 5′-UTR, intron, and 3′-UTR and as black boxes with arrowheads for the two exons. The N and C domains are demarcated by thick colored lines: green for the N domain and blue for the C domain (the C domain comprises parts of both exons). The gene length (1,092 nucleotides) and positions of polymorphic sites (prefixed with “5u” for 5′-UTR, “e1” for exon 1, “i” for intron, “e2” for exon 2, and “3u” for 3′-UTR) were determined from the full-length gene sequence alignment, such that insertions among inbred lines expanded the length of the B73 reference sequence. (Upper) Multivariate test statistic results for polymorphic sites plotted as a function of physical distance. For nonsynonymous SNP substitutions, the amino acid polymorphisms are indicated by their one-letter codes. (Lower) LD r2 estimates for each pair of polymorphic sites. Black lines and labels are meant to aid in visualizing LD among gene structures (e.g., “e1-i” indicates all pairwise comparisons between exon 1 and the intron).