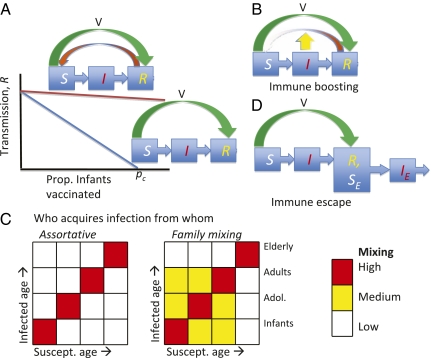
Fig. 1.
Factors influencing the dynamics of pertussis infection. (A) Scaling of transmission with vaccination rate for strongly immunizing (SIR) infections and infections with significant loss of immunity (SIRS). (B) Immune boosting, by exposure to currently circulating infection, could inhibit immunity loss (and hence the flow from R back to S) (5). (C) Patterns of population mixing and infection. Assortative mixing by age (Left matrix) could lessen the transmission impact of immune loss in older individuals, compared with more widespread age mixing (Right matrix) (13). (D) Novel genetic variants could escape immunity (12). In this cartoon, individuals immune to the prevailing pathogen genotype (in class R) are susceptible to an invading genotype (hence, they are also in class SE and can become infected with the genotype, moving into IE.