Fig. 1.
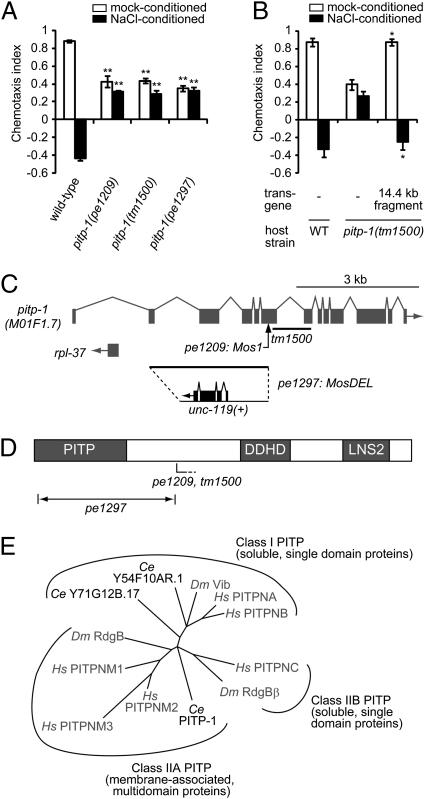
pitp-1 encodes a class IIA PITP. (A and B) Attraction behaviors to NaCl and chemotaxis plasticity in wild-type and pitp-1 mutant animals. Error bars represent SEM. (A) pitp-1 mutants show two phenotypes: decreased attraction to salt (mock-conditioned) and eliminated plasticity of chemotaxis (NaCl-conditioned). **P < 0.001 compared with wild-type, Dunnet test. (B) The two phenotypes of pitp-1(tm1500) mutants were fully rescued by introduction of a PCR-amplified 14.4-kb genomic fragment. *P < 0.01, t test. (C) Genomic organization of the pitp-1 locus. The Mos1 insertion in pe1209 is indicated by an arrow, and the tm1500 deletion is indicated by a line. In pe1297, the 2,951-bp region from second exon to the Mos1 insertion site in pe1209 was replaced by a 2.2-kb Caenorhabditis Briggsae unc-119(+) genomic DNA. (D) Schematic of the domain structures of PITP-1. The approximate positions of the mutations are indicated. PITP, DDHD domain (DDHD), and LNS2 domain (LNS2) are indicated. (E) Phylogenic analysis of full-length sequences of PITP orthologs. C. elegans PITPs are two class I PITPs (Y54F10AR.1 and Y71G12B.17) and a class IIA PITP (PITP-1). Other species are abbreviated as follows: Hs, Homo sapiens; Dm, Drosophila melanogaster. The dendrogram was generated with ClustalW and NJplot.