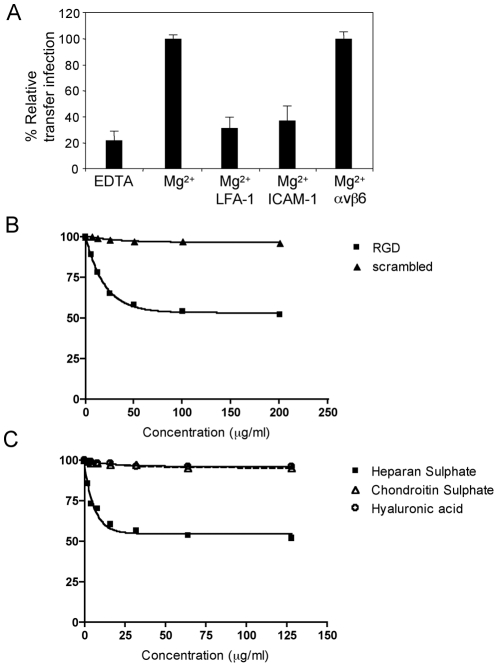
Figure 3. Molecules mediating B cell adhesion to epithelial cells.
B cell-epithelial cell adhesion was examined by transfer infection for cation, RGD or GAG usage. (A) EBV-infected B cells (24 h p.i.) and tonsillar epithelial cells were washed in Ca2+/Mg2+-free PBS. Co-culture was performed in binding buffer in the absence of cations (EDTA) or the presence of Mg2+, then under optimal cation conditions, B cells and epithelial cells were pre-incubated in blocking antibodies to LFA-1, ICAM-1 and a control αvβ6. B cells were washed off after 1 hour of co-culture and epithelial cell infection (GFP) was examined by flow cytometry after 24 hours. The % GFP +ve epithelial cells were plotted as the mean of triplicates relative to the optimal transfer infection conditions. (B) RGD peptide and a scrambled control peptide were titrated and pre-incubated with the B cells and epithelial cells under optimal cation conditions in binding buffer. Co-culture was performed for 1 hour and epithelial cell infection analysed as above. The mean % GFP +ve of triplicate epithelial cell infections were plotted against the peptide concentration. (C) The glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) heparan sulphate, hyaluronic acid and chondroitin sulphate were titrated as above. The mean % GFP +ve of triplicate epithelial cells infections were plotted against the GAG concentrations.