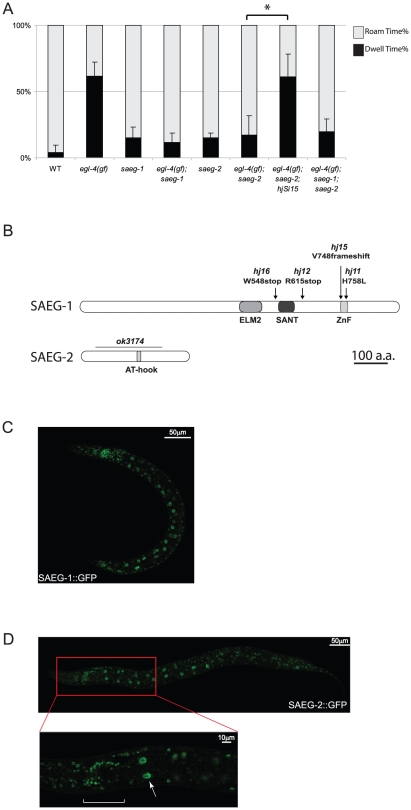
Figure 2. SAEG-1 and SAEG-2 act downstream of EGL-4 to control foraging behavior.
(A) Foraging behavior of wild-type (WT), egl-4, saeg-1 and saeg-2 mutant animals. Quantitation of behavior was performed as in Figure 1A. Data for WT and egl-4(gf) animals are the same as in Figure 1A. Total number of trials for all other strains: n = 5. (Mean±SD; pair-wise t-test, *, p<0.05). (B) Schematic representations of SAEG-1 and SAEG-2 protein. Conserved domains are indicated; ZnF, C2H2 zinc finger. Mutant alleles together with corresponding changes in protein coding sequences are indicated. The saeg-2(hj9) molecular lesion is not shown because it affects the splice donor site of intron 3. (C) Nuclear localization of SAEG-1::GFP fusion protein. Confocal image of a larval L4 stage egl-4(gf); saeg-1; Ex[saeg-1p::saeg-1::gfp] animal is shown. (D) Nuclear localization of SAEG-2::GFP fusion protein. Confocal image of a larval L4 stage saeg-2; hjSi15[saeg-2p::saeg-2::gfp] animal is shown. Inset shows the same animal at higher magnification, bracket indicates nuclei of neurons in the nerve ring and arrow indicates an intestinal nucleus.