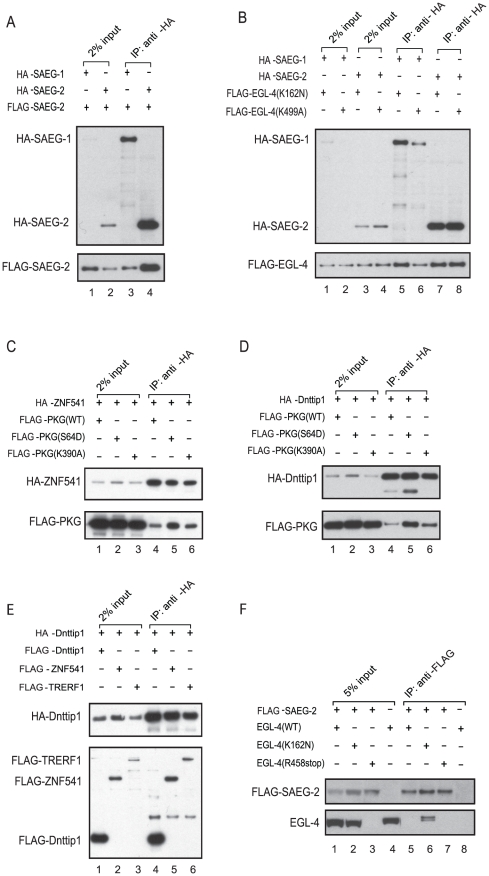
Figure 3. Physical interaction between EGL-4, SAEG-1, SAEG-2, and their mammalian orthologs.
(A) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged SAEG-2 (FLAG-SAEG-2) with HA-tagged SAEG-1 (HA-SAEG-1) or SAEG-2 (HA-SAEG-2) upon co-expression in Drosophila S2 cells. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged EGL-4 with HA-tagged SAEG-1 (HA-SAEG-1) or SAEG-2 (HA-SAEG-2) upon co-expression in Drosophila S2 cells. SAEG-1 and SAEG-2 associate with constitutively active (K162N) or kinase dead (K499A) EGL-4 when over-expressed. (C) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged wild-type (WT), constitutively active (S64D) or kinase dead (K390A) PKG-Iβ with HA-tagged ZNF541 after co-expression in HEK293 cells. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged wild-type (WT), constitutively active (S64D) or kinase dead (K390A) PKG-Iβ with HA-tagged Dnttip1 after co-expression in HEK293 cells. (E) Co-immunoprecipitation of FLAG-tagged Dnttip1, ZNF541 or TRERF1 with HA-tagged Dnttip1 after co-expression in HEK293 cells. (F) Preferential association of endogenous, constitutively active EGL-4(K162N) with FLAG-tagged SAEG-2 that was expressed at the endogenous level. Mutant animals carrying the egl-4(n479) allele did not express full length EGL-4 protein. Five independent experiments were performed and results from one representative experiment are shown.