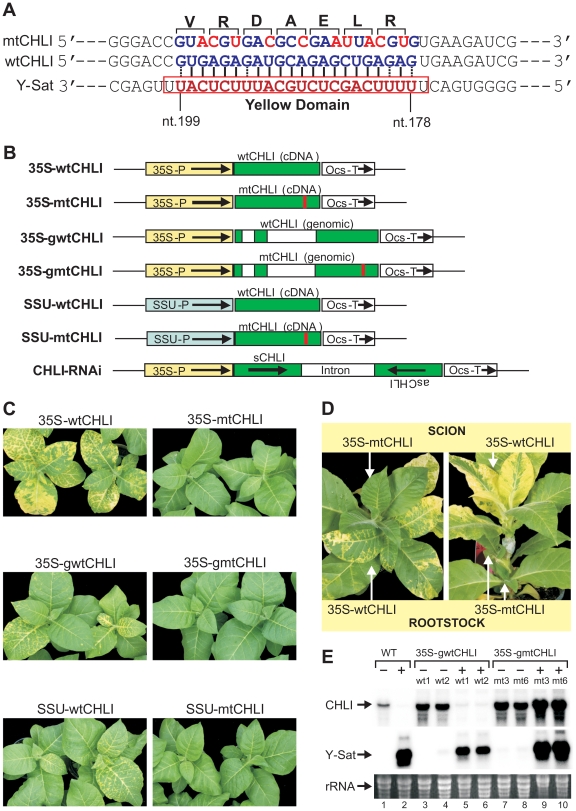
Figure 3. Transformation of N. tabacum with silencing-resistant CHLI constructs inhibits Y-Sat-induced yellowing symptoms.
(A), Ten translationally silent nucleotide changes (shown in red) were introduced to the CHLI sequence to disrupt the binding between Y-Sat siRNAs and the CHLI mRNA. The amino acid sequence is given above. (B), Schematic diagrams of wild-type (wt) and mutant (mt) CHLI overexpression constructs plus the RNAi construct used for tobacco transformation. 35S-P, cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter; SSU-P, tobacco rubisco small subunit promoter; Ocs-T, Agrobacterium tumefaciens octopine synthase 3′ terminator region. Empty boxes represent introns of the CHLI genomic sequence; red lines indicate the sequence-modified region. The RNAi construct contains a partial (571 bp) sense (sCHLI) and antisense (asCHLI) CHLI sequence spanning the Y-Sat target site. (C), Tobacco plants transformed with wild-type CHLI constructs develop the yellowing symptoms upon CMV Y-Sat infection, but those transformed with mutant CHLI constructs do not show the symptoms. The picture was taken 20 days post-inoculation. Some of the CMV Y-Sat-infected wtCHLI plants showed a delayed onset of the yellowing symptoms, presumably because the CHLI transgene provided additional CHLI mRNA to the endogenous transcript, causing a reduction in the rate of CHLI silencing. (D), An example of reciprocal grafting between CMV Y-Sat-infected mtCHLI plants and wtCHLI plants. Only the wtCHLI scion or root stock developed the yellowing symptoms. (E), Northern blot hybridization shows that the CHLI mRNA expressed from the mtCHLI construct is resistant to Y-Sat-induced silencing. The ‘+’ symbol indicates samples from plants infected with CMV Y-Sat, while the ‘−’ symbol identifies samples extracted from plants prior to CMV Y-Sat infection. wt1, wt2, mt3 and mt6 are line numbers for the 35S-gwtCHLI and 35S-gmtCHLI transformants. Gel lane numbers are given at the bottom.