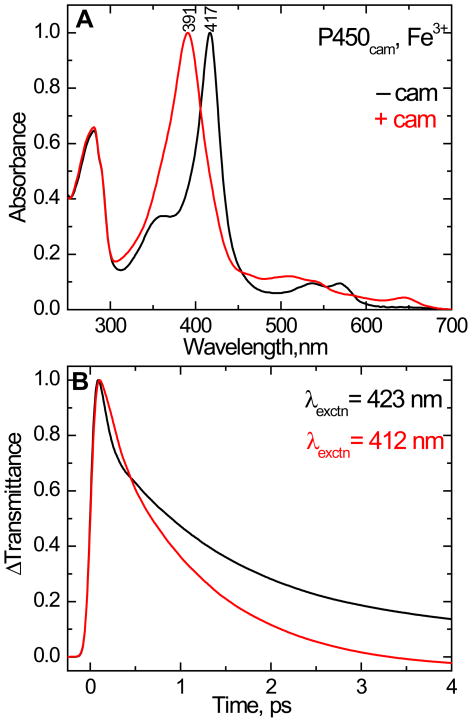
Figure 2.
(A). The normalized equilibrium absorption spectra of ferric cytochrome P450cam in 50 mM KPi buffer with 150 mM KCl at pH 7.4. The absorption band peaking at 417 nm is the camphor-free form and the spectrum peaking at 391 nm is the camphor-bound form. (B). Normalized femtosecond time-resolved optical transmittance of cytochrome P450cam in the camphor-free (black) and camphor-bound (red) states. The excitation wavelength is 412 nm for camphor-bound (red) and 423 nm for camphor-free (black). The kinetic traces show a bleach followed by a recovery to equilibrium (ΔT > 0) and fitted with bi-exponential decay starting from 200 fs. The time constants (τ) and amplitudes (a) used as fitting parameters for the camphor free species are τ1= 56 fs (a1 = 0.79), τ2= 1.5 ps (a2 = 0.18) and offset = 0.02 and for camphor bound complex τ1= 140 fs (a1 = 0.36), τ2= 1.1 ps (a2 = 0.67) and offset = −0.03. The shortest time constant and its amplitude are distorted due to convolution with the coherence coupling signal.