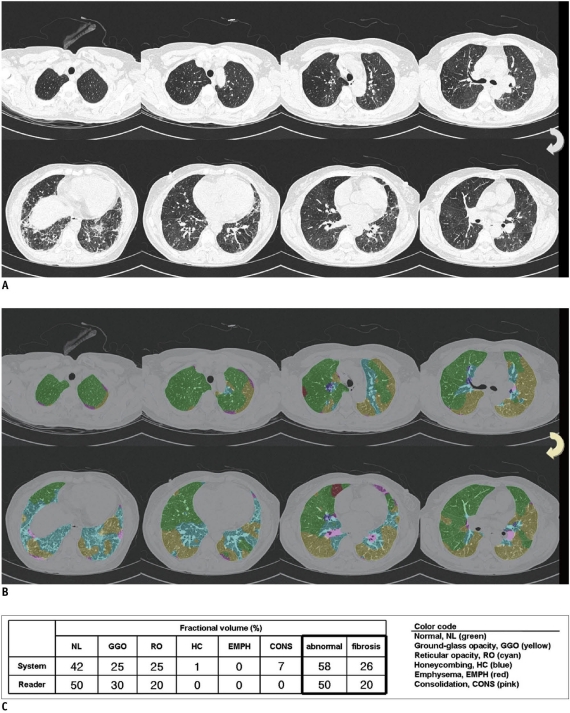
Fig. 2.
55-year-old woman who had pathologically proven nonspecific interstitial pneumonia.
A. CT images showed basal ground glass and reticular opacities with no areas of honeycombing. Reader 1 gave five-point rating scale as 2, thus suggesting probable nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Reader 2 gave five-point rating scale as 1, thereby suggesting definite nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. B. System interpreted approximately one-half of lung volume as ground glass and reticular opacities. System also detected some areas of consolidation and honeycombing. Value of prob (event)* was < 0.01, thus classifying CT images as nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. Pathology also indicated nonspecific interstitial pneumonia. C. System determined 58% of whole lung as abnormal, whereas radiologist regarded 50% as abnormal lung. Extent of fibrosis was 26% according to system, and 20% according to radiologist.
*Logistic prediction equation was:
ln(prob(event)/[1-prob(event)]) = 0.404 HC + 0.178 GGO + 0.181 RO - 0.010 HC × RO - 0.006 GGO × RO - 0.064 CONS × GGO - 4.347
where, prob(event) < 0.50 was nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and prob(event) ≥ 0.50 was usual interstitial pneumonia.