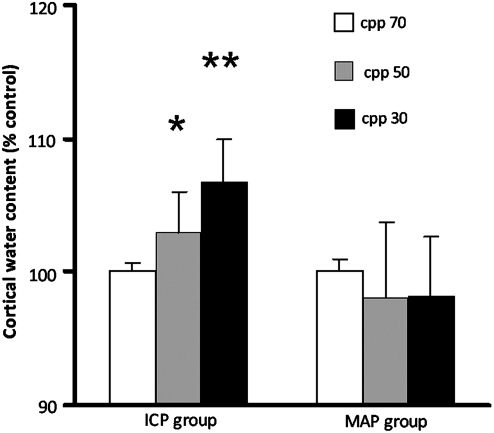
FIG. 4.
Cortical water content in percentage of controls as measured by dry/wet weight in the rat parietal cortex at cerebral perfusion pressures (CPP) of 70, 50, and 30 mm Hg, by either intracranial pressure (ICP) increase (ICP group), or mean arterial pressure (MAP) reduction (MAP group). Decreasing CPP from 70 to 50 and 30 mm Hg by high ICP increased cortical water content significantly (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, respectively) (n=3 rats for each CPP), compared to a normal CPP of 70 mm Hg (n=6 rats). In the MAP group cortical water content was no different from controls (n=3 rats for each CPP level). Data are presented as mean±standard error of the mean (SEM). The control water content value at a CPP of 70 mm Hg was 72.9±0.47% (n=10) by scooping, which was significantly lower than the value of 79.58±0.76% (n=5) obtained by removal of the brain from the calvarium.