Figure 2.
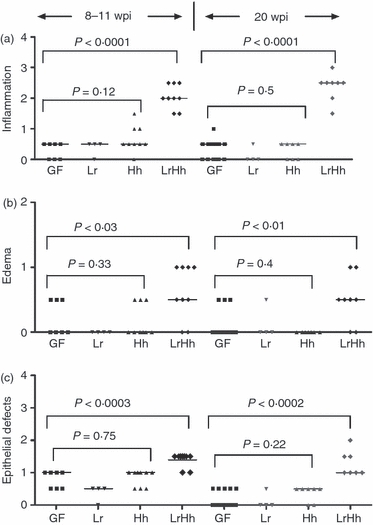
Germ-free B6.129P2-IL-10tm1Cgn (IL-10−/−) mice were colonized at 6–8 weeks of age with Lactobacillus reuteri (Lr) Helicobacter hepaticus (Hh) or L. reuteri followed in 1 week by H. hepaticus (LrHh) and killed and examined post-mortem at 8–11 or 20 weeks post-infection (p.i.). Median scores were significantly higher for (a) inflammation (P < 0.0001; P < 0.0001) (b) submucosal oedema (P < 0.03; P < 0.01) and (c) epithelial defects (P < 0.0003; P < 0.0002) at the caecal–colonic junction of IL-10−/− mice co-infected with L. reuteri and H. hepaticus (LrHh) for 8–11 or 20 weeks p.i. (respectively) compared with germ-free (GF) mice or mice mono-associated with L. reuteri (Lr) or H. hepaticus (Hh). There were no significant differences in inflammation, submucosal oedema or epithelial defects in mice that were germ-free or mono-associated with either L. reuteri or H. hepaticus (analysis of variance P-values as shown).
