Figure 4.
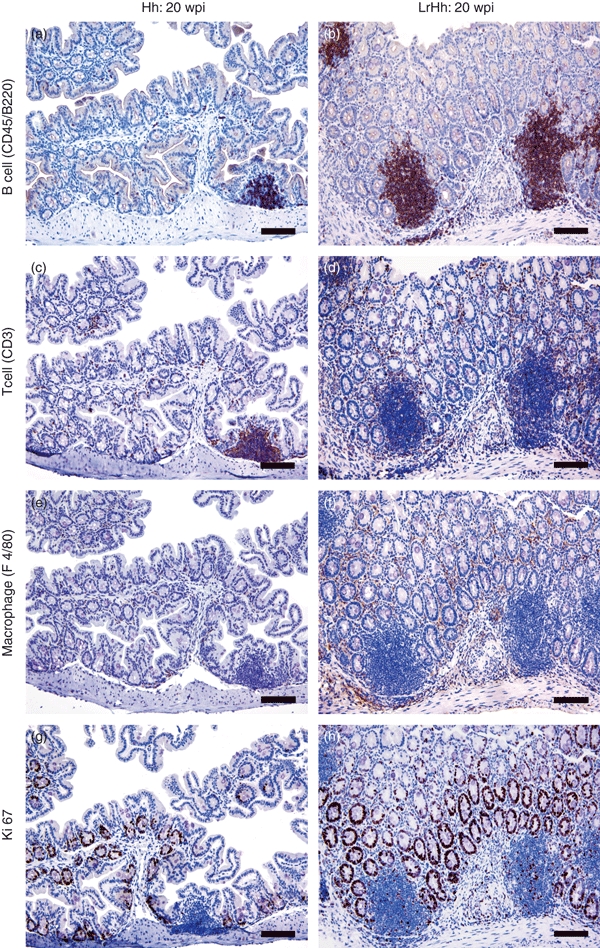
Immunohistochemistry to phenotype B cells (CD45/B220+), T cells (CD3+), macrophages (F4/80+) and proliferating cells (Ki67+) at the caecal–colonic junction of gnotobiotic IL-10−/− mice infected with Helicobacter hepaticus alone (Hh) or with H. hepaticus and Lactobacillus reuteri (LrHh) for 20 weeks post-infection (20 wpi). Germ-free controls and mice mono-associated with L. reuteri alone were similar to H. hepaticus alone and are not shown. Mice with H. hepaticus alone had a few foci of lymphoid aggregates and some distinct lymphoid follicles that contained mostly B cells (a), fewer T cells (c) and sparse macrophages (e). Ki67 activity was minimal and was restricted to the acini and crypts (g). The co-infected mice (LrHh) developed prominent lymphoid follicles that were predominantly B cells (b), with T cells surrounding the germinal centres (d). Small numbers of B cells, considerable numbers of T cells and macrophages (f) were also increased in the lamina propria. Intraepithelial T lymphocytes and macrophages were also increased. Ki67 activity was prominent in the glands (h), within lymphoid follicles and in the inflammatory infiltrates. Magnification × 200 (bar = 80 μm).
