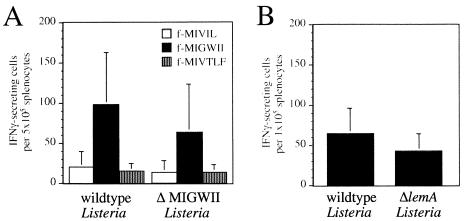
FIG. 5.
Infection of mice with ΔlemA mutant strains of L. monocytogenes results in the activation of fMIGWII-specific T cells. (A) Groups of C.B10 mice (two to four) were given intravenous injections of 103 CFU of either 10403s (wild-type listeriae) or SD9-1 (ΔMIGWII listeriae). Six days later, the mice were sacrificed, and the number of fMIVIL-, fMIGWII-, and fMIVTLF-specific T cells present in the spleen of each mouse was determined by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay. The average number of IFN-γ-secreting cells per 5 × 105 splenocytes ± standard deviation is shown. Data compiled from three separate experiments are shown. (B) Groups of four C.B10 mice were infected with 103 CFU of either 10403s or NR1-1578 (ΔlemA). Six days later, the mice were sacrificed, and the number of fMIGWII-specific T cells present in the spleen each mouse was determined by IFN-γ ELISPOT assay.