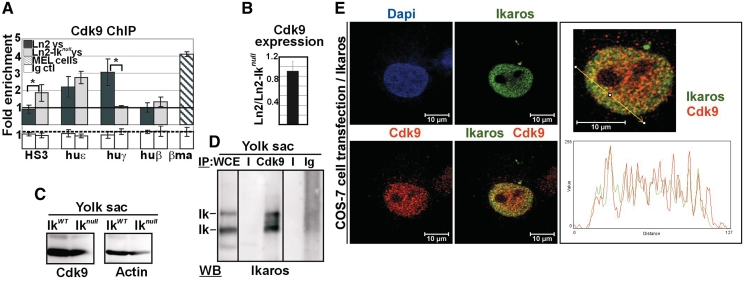
Figure 6.
Ikaros-mediated recruitment of Cdk9 to the huγ-genes in yolk sac EryC. (A) ChIP on ln2 and ln2-Iknull yolk sac EryC carried out with Cdk9 antibodies; fold enrichments (y-axis) were calculated as described in Figure 1E and are plotted as the mean ± SD of the measurements; a value of 1 (dashed line) indicates no enrichment; *P ≤ 0.05 by Student’s t-test; huε, huε-promoter; huγ, huγ-promoters; huβ, huβ-promoter; βma, βmajor promoter; dark gray bars: ln2 yolk sac EryC; light gray bars: ln2-Iknull yolk sac EryC; dark gray dashed bars: MEL cells; white bars: isotype-matched Ig (Ig ctl); (B) RT–qPCR of Cdk9 gene transcripts performed on equal amounts of ln2 and ln2-Iknull yolk sac EryC; transcript quantification was calculated according to Pfaffl (73) using mouse Actin cDNA as internal control; ln2/ln2-Iknull ratios are plotted as the mean ± SD of the measurements; n = 6; (C) WB performed on total cell lysates prepared from wild type or Iknull yolk sac EryC with Cdk9 or Actin antibodies; (D) protein co-IP of total cell lysates prepared from ln2 yolk sac EryC; cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with Cdk9 antibodies or isotype-matched Ig and WB were carried out with Ikaros antibodies; WCE: yolk sac EryC total cell lysate; (E) Confocal immunofluorescence of COS-7 cells expressing Flag/HA-Ikaros protein; cells were stained with mouse antibodies to the HA tag and with rabbit antibodies to Cdk9; the secondary staining was carried out with FITC-conjugated anti-mouse as well as TR-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies; a single COS-7 cell is shown where Ikaros is detected as green signals, Cdk9 as red signals, and Ikaros-Cdk9 co-localization as yellow signals in the magnified merged image; line profile plots of Ikaros (in green) and Cdk9 (in red) were obtained by the WCIF ImageJ(®) program (NIH).