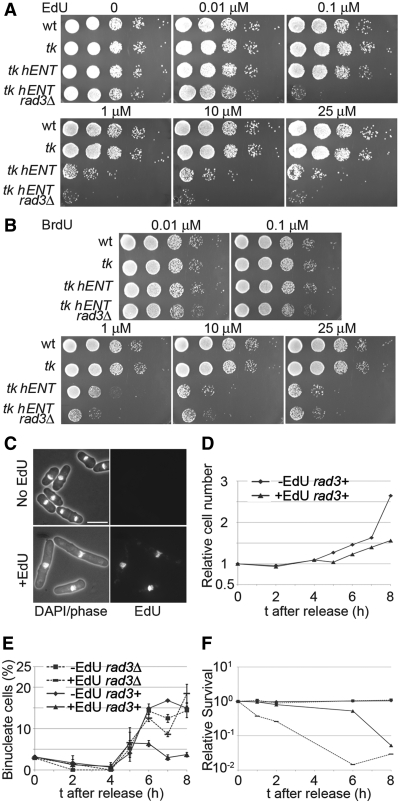
Figure 2.
Effects of EdU incorporation on viability and cell cycle progression. (A) Serial dilutions (10-fold) of wild-type (P2), tk (adh1:tk, P2471), tk hENT (adh1:tk adh1:hENT1,P2470) and tk hENT rad3Δ (adh1:tk adh1:hENT1 rad3Δ, P2472) cells were spotted on to YE3S plates containing EdU at the indicated concentrations, (B) As (A) but cells were spotted onto YE3S plates containing BrdU at the indicated concentrations, (C) Cell elongation following growth in EdU. Lower panels show tk hENT (adh1:tk adh1:hENT1 (P2470)) cells grown in 1 μM EdU (YE3S medium) for 5 h and imaged following DAPI staining and EdU detection; upper panels show control cells from a culture lacking EdU. Bar = 10 µm, (D) Effect of EdU on cell division. tk hENT [adh1:tk adh1:hENT1 (P2470)] cells were arrested in G1 by growing in EMM-N for 16 h at 26°C, then released from the cell cycle block in EMM+N medium at 32°C in the presence (1 μM) or absence of EdU and cell concentrations were monitored. The effect of EdU on cell division of rad3Δ cells is shown in Supplementary Figure S2. (E and F) As (D) except that rad3+ [adh1:tk adh1:hENT1 (P2470)] and rad3Δ [adh1:tk adh1:hENT1 rad3Δ (P2472)] strains were released from a G1 block and the percentage of binucleate cells (E) and cell viabilities (F) were determined.