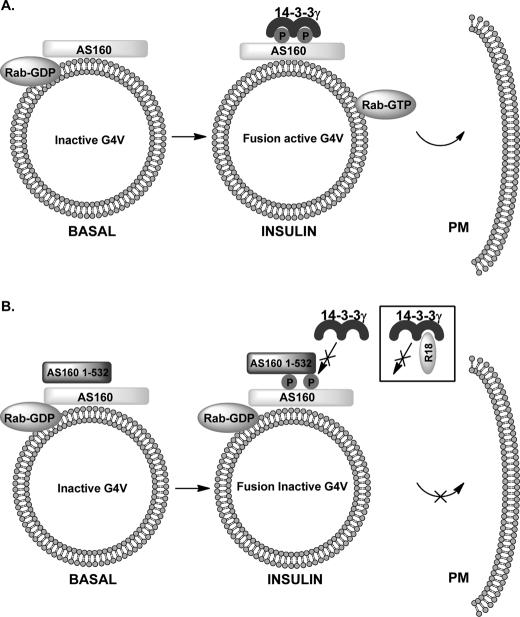
FIGURE 6.
Model for inhibitory effects of AS160 N-terminal PTB domain constructs and 14-3-3-quenching reagents on GLUT4 vesicle fusion. A, insulin-stimulated generation of fusion-active GLUT4 vesicles (G4V). Insulin action leads to AS160 phosphorylation and 14-3-3γ binding and consequently generation of a GLUT4 vesicle Rab in an active GTP-loaded form. B, proposed mechanism for fusion inhibition by the N-terminal tandem PTB domain construct AS160(1–532). It is proposed that heterodimer formation with full-length AS160 prevents 14-3-3γ binding. The R18 peptide prevents 14-3-3γ binding through direct quenching reaction. PM, plasma membrane.