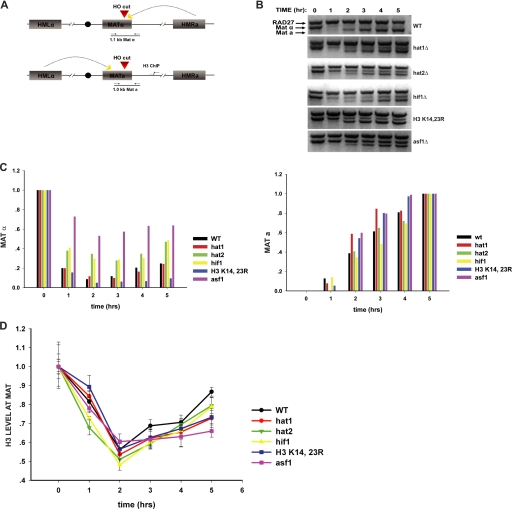
FIGURE 2.
Impact of NuB4 complex and histone H3 mutations on DNA repair-linked chromatin reassembly. A, schematic diagram of the inducible HO-mediated mating type switch system used to model recombinational DNA repair. Locations of primers used for PCR analysis of the double strand break at the MAT locus and for ChIP analysis of histone H3 disassembly and reassembly are indicated. B, introduction and repair of the double strand break at the MAT locus was monitored by PCR assay in the indicated strains. Galactose was added at the 0-h time point and glucose was added at the 2-h time point. Reaction products were resolved on a 1.5% agarose gel and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. The migration of the MATα- and MATa-specific bands is indicated. Amplification of a region of the RAD27 locus was used as a control. C, quantitation of double strand break formation and repair. Stained agarose gels were photographed and the MATα, MATa, and RAD27 bands were quantitated using one-dimensional Image Analysis software (Kodak). MATα and MATa fragments were normalized to the RAD27 fragment. The MATα and MATa fragments were plotted relative to the 0- and 5-h time points, respectively. D, ChIP analysis of the abundance of histone H3 at a site 600 bp from the double strand break at the MAT locus. The graph shows a comparison of the indicated NuB4 complex or histone H3 mutant to a wild type strain and an asf1Δ strain. Histone H3 levels were normalized to H3 levels at the SMC2 locus. Subsequent time points are normalized to the 0-h time point.