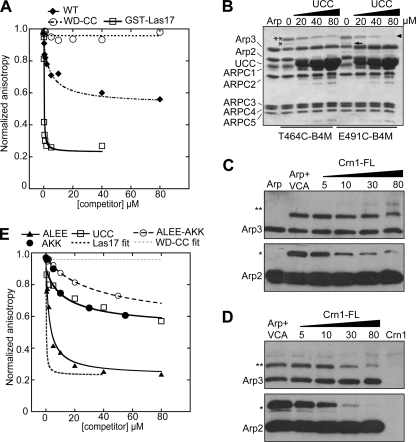
FIGURE 4.
Crn1 interacts directly with Arp2/3 complex through its CA region and competes with VCA. A and E, fluorescence anisotropy competition assay to measure interaction between Arp2/3 complex and Crn1 constructs. Increasing concentrations of Crn1, Crn1-WD-CC, Crn1-ALEE, Crn1-AKK, Crn1-ALEE-AKK, Crn1-UCC, or GST-Las17-VCA were equilibrated with 60 nm ScArp2/3 complex and 50 nm SpWsp1-Rh-VCA, and the anisotropy was measured. Data were fit as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The KD for the Crn1-ALEE-AKK was estimated by assuming saturation at a normalized anisotropy value of 0.6, as observed for wild-type Crn1. B, Coomassie Brilliant Blue-stained gel of 5.0 μm Bos taurus Arp2/3 complex cross-linked to 10 μm T464C-B4M or E491C-B4M in the presence of increasing concentrations of Crn1-UCC. Cross-linked bands are labeled as follows: two asterisks, Arp3xT464C-B4M-VCA; single asterisks, Arp2xT464C-B4M-VCA; arrowhead, Arp3xE491C-B4M-VCA; arrow, Arp2xE491C-B4M-VCA. Supplemental Fig. S5 shows that Crn1 activates B. taurus Arp2/3 complex. C and D, Western blots of cross-linking reactions with T464C-VCA (C) or E491C-VCA (D). Conditions were identical to B, except that increasing concentrations of Crn1 (full length (FL)) were added to the reaction. The top row shows anti-Arp3 blots, and the bottom row shows anti-Arp2 blots.