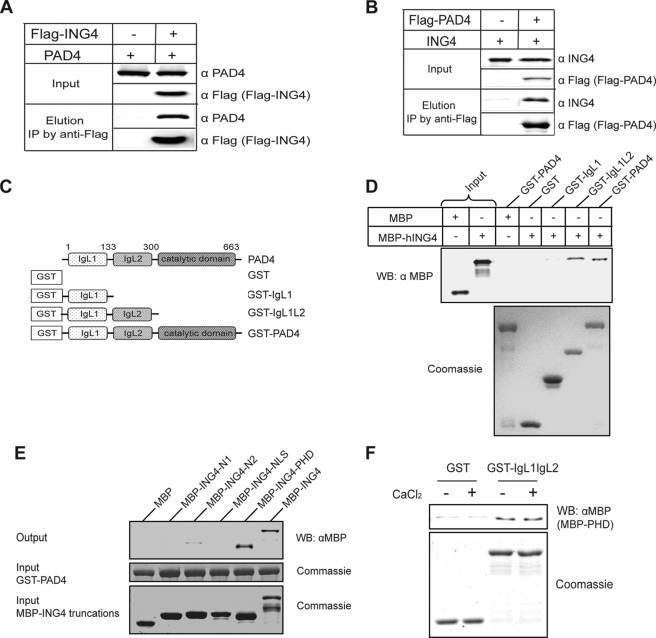
FIGURE 2.
PAD4 binds ING4, independent of added calcium. A, PAD4 coimmunoprecipitates (IP) with FLAG-ING4 from HEK 293T cells co-expressing PAD4 and FLAG-ING4. B, ING4 coimmunoprecipitates with FLAG-PAD4 from HEK 293T cells co-expressing FLAG-PAD4 and ING4. C, shown is a schematic of PAD4 deletion mutants. D, the N-terminal IgL of PAD4 was sufficient for the interaction with ING4. Immobilized on the glutathione resin, the full-length and truncations of PAD4 were used to pull down MBP-ING4. The bound MBP-ING4 was detected by Western blot (WB) using an anti-MBP antibody (α MBP). E, the PHD domain of ING4 is the major region involved in PAD4 binding. PAD4 were immobilized on the glutathione resin and incubated with full-length ING4 or its deletion mutants (Fig. 1C). The assay was performed using the same methods as D. F, the PAD4 IgL domains directly interact with the PHD domain of ING4 in a calcium-independent manner. Immobilized on the glutathione resin, GST or GST-IgL was incubated with MBP-PHD in the absence or presence of 2 mm CaCl2. The assay was performed as in D and E.