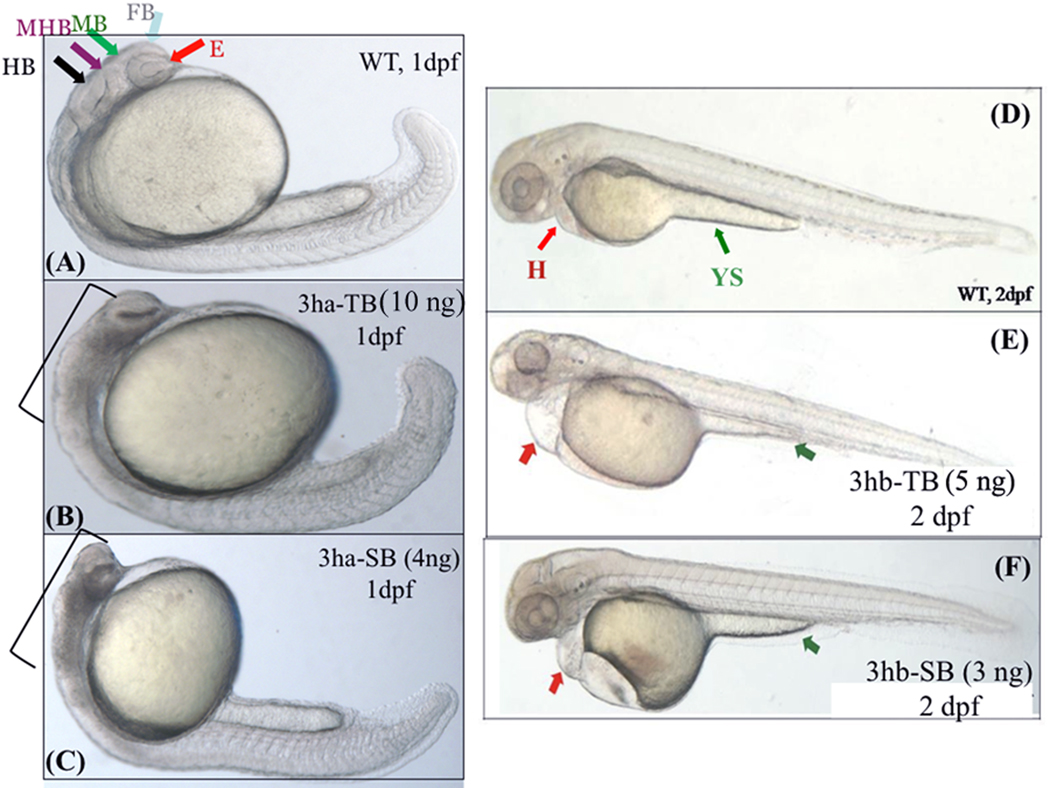
FIG. 5. Each of the eif3h morphants show distinct embryonic phenotypes.
Shown are representative morphant phenotypes obtained by injecting either TB or SB morpholino (MO) for eif3ha (3ha-TB or 3ha-SB) at 1 dpf (B and C) and for eif3hb (3hb-TB or 3hb-SB) at 2 dpf (E and F). In each case, an uninjected wild-type (WT) control (panels A and D) is also included. In panel A, different regions of the normal brain in a WT embryo at 24 hpf are shown: eye (E), forebrain (FB), midbrain (MB), midbrain-hindbrain boundary (MHB), and hindbrain (HB) as indicated by different colored arrows. For the eif3ha morphants (~100%, n ~ 200), following injection of either TB MO (panel B) or SB MO (panel C), gross disruption of all the brain regions are shown using brackets. For the eif3hb morphants (90 – 95%, n ~ 200) at 2 dpf obtained with either TB MO (panel E) or SB MO (panel F), specific defects in the form of edema seen around the heart region (H) and regression of yolk stalk (YS) are indicated with the red and green arrows, respectively.