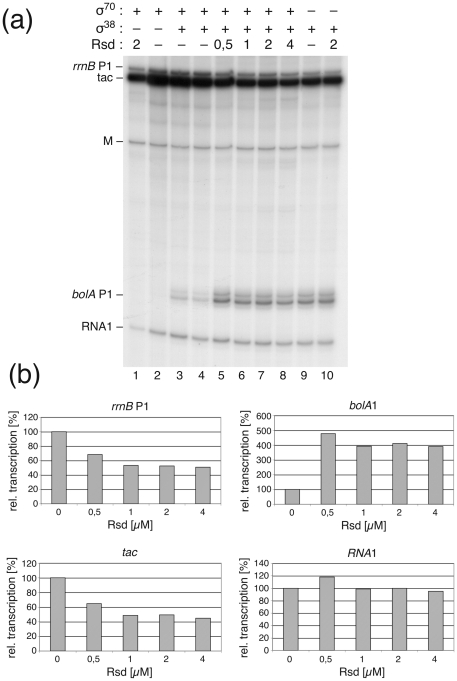
Figure 4. Effects of Rsd on in vitro transcription under competitive conditions.
(a) Products from in vitro transcription reactions performed with RNA polymerase holoenzymes (20 nM) reconstituted with either 30 nM of σ70 or σ38 subunits (indicated by +) were separated on denaturing gels. Transcription products originating from the different promoters present on the template vector pSH666-1 (rrnB P1, tac, bolA P1, RNA 1) are indicated at the left margin of the autoradiogram. M denotes the position of a loading standard. The amount of Rsd (µM), when present in the reaction mixture, is given above the gel lanes. (b) Quantitative evaluation of the amounts of transcripts for promoters rrnB P1, bolA1, tac, and RNA 1 shown in (a, lanes 3 to 8). Bars represent relative transcripts as a function of the Rsd concentration present in the reaction mixture. Transcripts in the absence of Rsd (the mean from lanes 3 and 4) are set to 100%. The experiment was repeated twice with similar results.