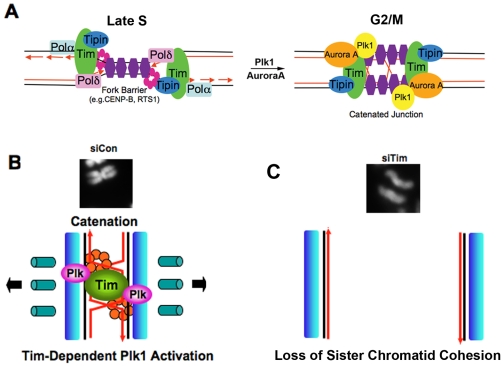
Figure 8. Tim coordinates replication termination with mitotic kinase activation.
A) Model of Tim coordinating replication termination with mitotic kinase activation. Replication forks approach fork-blocking proteins (blue) in S phase lead to the formation of recombination structures in G2. Tim is required for the formation of the DNA recombination structure and the recruitment of Plk1 and Aurora A, as demonstrated at centromeric DNA. B) Metaphase chromosome cohesion is established through Tim-dependent DNA recombination or termination structures (X-structure), which leads to the activation of mitotic kinases (e.g. Plk1). C) Tim depletion causes a loss of DNA catenation, loss of Plk1 recruitment to centromere repeats, loss of Plk activation, and loss of sister-chromatid cohesion.