Figure 6.
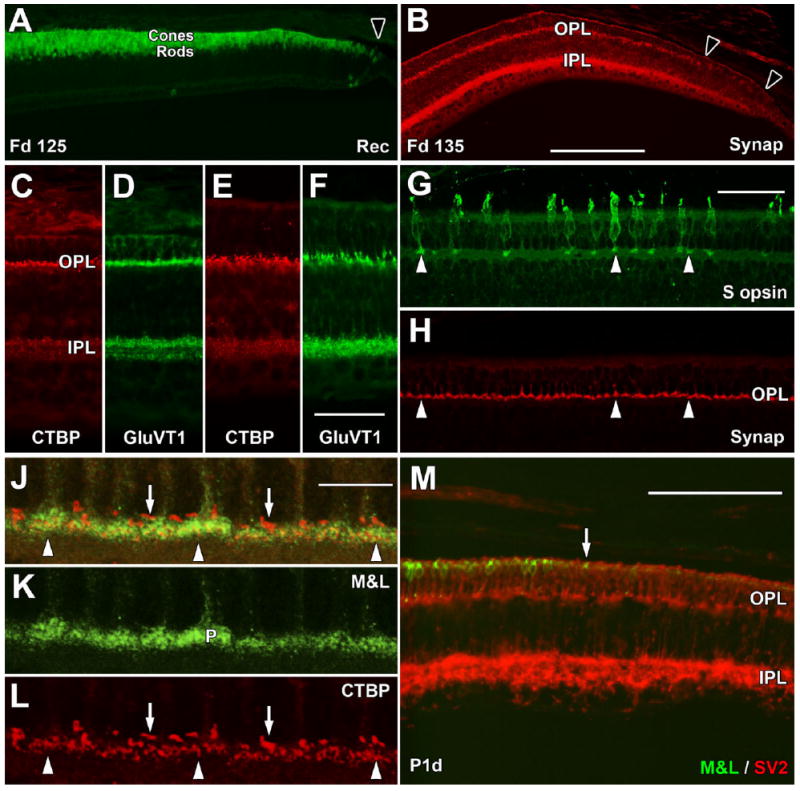
Late fetal and postnatal expression of synaptic markers. A: The far periphery of the Fd 125 retina contains a single layer of Rec+ cones and multiple deep Rec+ rods. Rec labeling extends to the edge of the retina (arrowhead). B: The far periphery at Fd 135 has Synap labeling in the IPL to the retinal edge (right arrowhead). In the OPL, there is a dense band of Synap+ cone pedicles, but these become sparse beyond the left arrow. C–F: By Fd 135, CTBP2 and GluVT1 prominently label the OPL and IPL in central (C,D) and far peripheral (E,F) retina. G,H: At Fd 135, cone pedicles of peripheral S+ cones (G, arrows) label for Synap (H, arrows), as do unlabeled M&L+ cones. J–L: Confocal images of central Fd 135 retina showing green M&L+ cone pedicles (J,K) and red CTBP2+ synaptic ribbons (J,L). The cone pedicles contain many thin short ribbons (arrowheads), whereas single, long, thicker ribbons occupy unlabeled spaces above the cone pedicles (arrows), presumably within the rod spherules. M: The temporal retinal edge (to the right) at birth has M&L+ cones (arrow) close to, but not at, the edge. SV2+ cones reach the edge, as does the SV2+ labeling in the IPL. A magenta-green copy is available as Supporting Information Figure 2. Scale bars = 200 μm in B (applies to A,B); 50 μm in F (applies to C–F); 50 μm in G (applies to G,H); 10 μm in J (applies to J–L); 100 μm in M.
