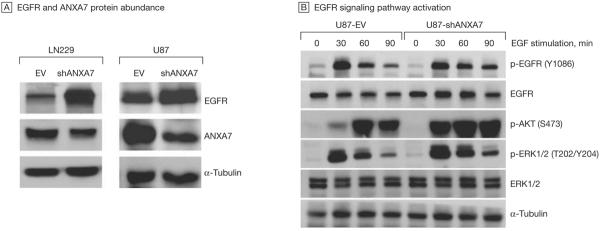
Figure 5. ANXA7 Knockdown and EGFR Protein Abundance and EGFR Signaling.
A, Knockdown of annexin A7 (ANXA7)—mimicking a hemizygous gene loss and thus haploinsufficiency—via ANXA7-targeting short hairpin RNA (shRNA) (shANXA7) using transient plasmid-based transfection (LN229) or stable, retroviral transduction (U87) increases epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) protein abundance compared with cells transfected with empty backbone control vector (EV) only, as assessed by immunoblotting. The α-tubulin protein was used as a loading control. Displayed blots are representative of multiple experiments. B, Total and phosphospecific EGFR, AKT, and ERK1/2 protein abundance in U87-shANXA7 vs U87-EV cells based on immunoblotting. Sustained EGFR autophosphorylation at Tyr 1086 (Y1086) and increased and sustained activating phosphorylation of AKT at Ser473 (S473) and ERK1/2 at Thr202/Tyr204 (T202/Y204) in shANXA7 compared with EV cells.