Figure 4. HKa accelerates the onset of EPC senescence and suppresses telomerase activity.
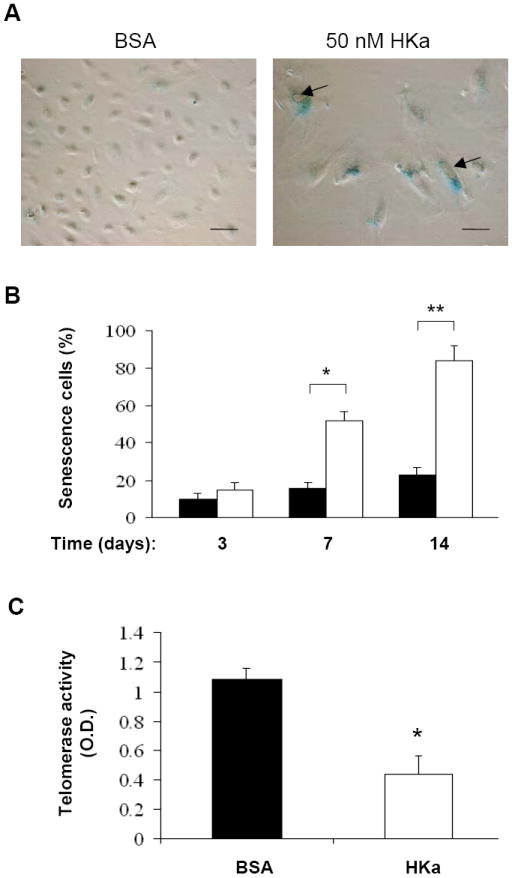
(A) Representative photomicrographs of SA-β-gal-positive EPCs (40 × magnifications). EPCs were cultured in the presence of 0.1% BSA or 50 nM HKa for 14 days. Culture medium was replaced every two days. SA-β-galactosidase activity of EPCs was analyzed as described under Materials and Methods. Scale bar represents 50 μm. Arrows indicate intracellular vacuoles. (B) Percentage of senescent cells was shown. EPCs were cultured in the presence of 0.1% BSA (open columns) or 50 nM HKa (grey columns) for the indicated period of time. The number of SA-β-gal-positive EPCs (senescent cells) was counted (n=6). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 v.s. BSA. (C) Effect of HKa on EPC telomerase activity. After EPCs were cultured in the presence of 0.1% BSA or 50 nM HKa for 14 days, telomerase activity was measured as described under the Materials and Methods. Data are mean ± SEM, n=4. *P < 0.001 vs. BSA.
