Figure S1.
C. elegans SAS-6 Characterization, Related to Figure 1
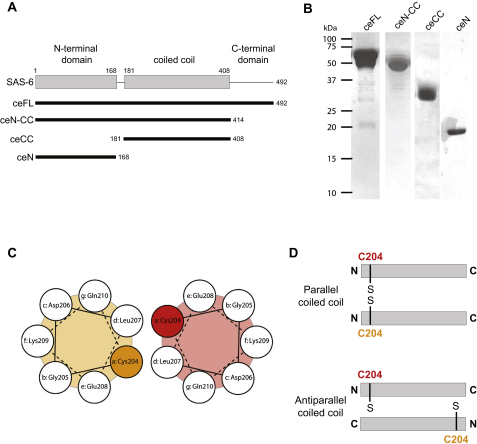
(A) Schematic representation of C. elegans SAS-6 and fragments used in this study. ceFL: full-length (amino acids 1–492), ceN-CC: N-terminus plus coiled coil (amino acids 1–414), ceCC: coiled coil (amino acids 181–408); ceN: N-terminus (amino acids 1–168).
(B) Sections of reducing and Coomassie-stained SDS-PAGE showing final purification products for the indicated recombinant proteins. From left to right: SAS-6 full-length (ceFL), ceN-CC (residues 1–414), ceCC (residues 181–408) and ceN (residues 1–168). Approximate molecular weights from in-gel markers are shown.
(C) Helical wheel representation of the SAS-6 coiled-coil domain in the vicinity of Cys204 in a two-stranded parallel configuration. The predicted heptad repeat (denoted a to g) and the residues occupying its position are indicated.
(D) Relative location of the Cys204 sulfur group on ceCC for a parallel or antiparallel coiled coil configuration. Efficient disulphide bridge formation is possible only in the parallel in-register coiled coil configuration.