Figure 3.
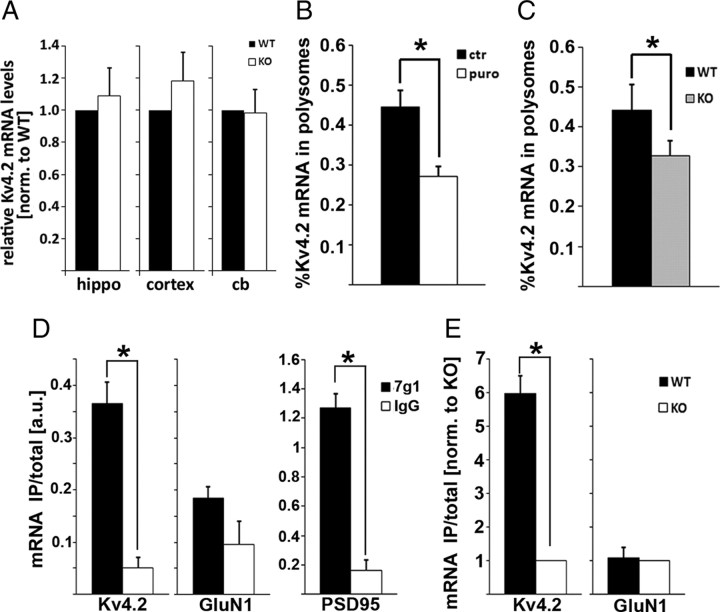
Kv4.2 mRNA translation is reduced in synaptic fractions from Fmr1 KO cortices. A, qRT-PCR analysis of Kv4.2 mRNA levels in different brain regions: hippocampus (hippo) (n = 4, p = 0.648, paired t test), cortex (n = 4, p = 0.372, paired t test), and cerebellum (cb) (n = 4, p = 0.926, paired t test) shows no significant difference between WT and KO. mRNA levels were normalized to tubulin mRNA. B, Polysome association of Kv4.2 mRNA in cortical synaptoneurosomes is puromycin sensitive, suggesting that Kv4.2 mRNA in these fractions is actively translated (n = 4, *p = 0.026, paired t test). C, Association of Kv4.2 mRNA with puromycin-sensitive fractions is significantly reduced in Fmr1 KO (n = 6, *p = 0.04, paired t test). D, E, Kv4.2 mRNA associates with FMRP in vivo in forebrain. D, qRT-PCR analysis of FMRP-specific coimmunoprecipitations from WT brain shows that Kv4.2 mRNA and the positive control PSD95 are significantly enriched compared with IgG control, whereas the negative control GluN1 shows no significant enrichment (n = 3; Kv4.2, *p = 0.040; GluN1, p = 0.147; PSD95, *p = 0.007; paired t tests). E, Specific enrichment of Kv4.2 mRNA, but not GluN1 mRNA, was also detected in FMRP-specific immunoprecipitations from WT and Fmr1 KO lysates (n = 3; Kv4.2, *p = 0.015; GluN1, p = 0.84; paired t tests).