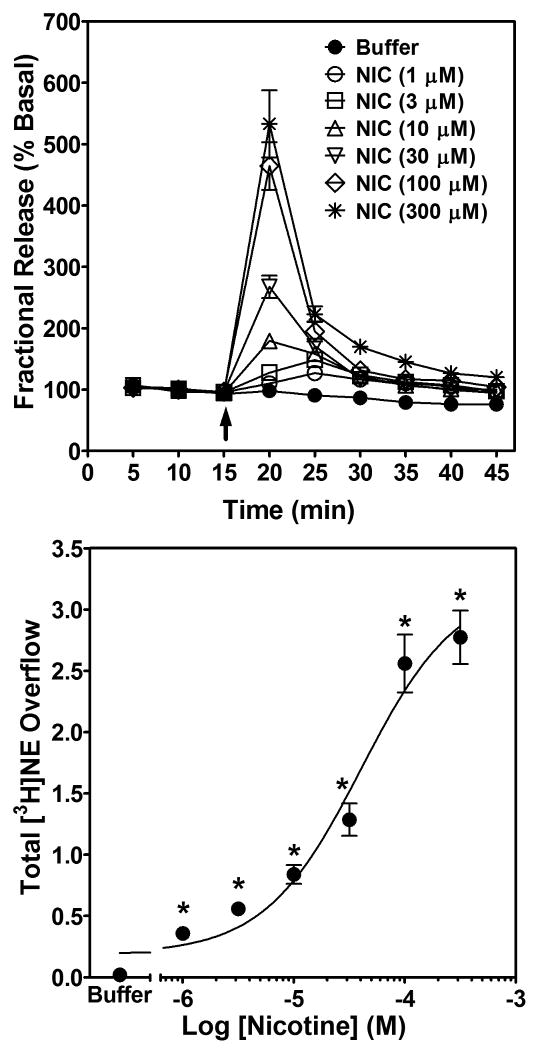
Fig. 2. Time course and concentration dependence of nicotine-evoked fractional [3H]NE release (top) and nicotine-evoked [3H]NE overflow (bottom) from superfused rat hippocampal slices.
Hippocampal slices were superfused in the absence or presence of a single concentration (1-300 μM) of nicotine for 30 min. Arrow indicates the time point at which nicotine was added to the superfusion buffer. Each experiment included a buffer control condition in which one slice was superfused with buffer only and fractional [3H]NE release (top) and [3H]NE overflow (bottom) determined. Fractional release data are expressed as a percentage of basal (mean ± SEM), n = 19 rats. Basal fractional release was 0.44 ± 0.004 as percentage of tissue-[3H] content. Fractional release data were used to calculate [3H]NE overflow data, which are expressed as mean ± S.E.M. total [3H]NE overflow as a percentage of tissue-[3H] content. n = 19. The concentration-response curve for nicotine was generated using nonlinear regression. * indicates difference from buffer control, p < 0.05.