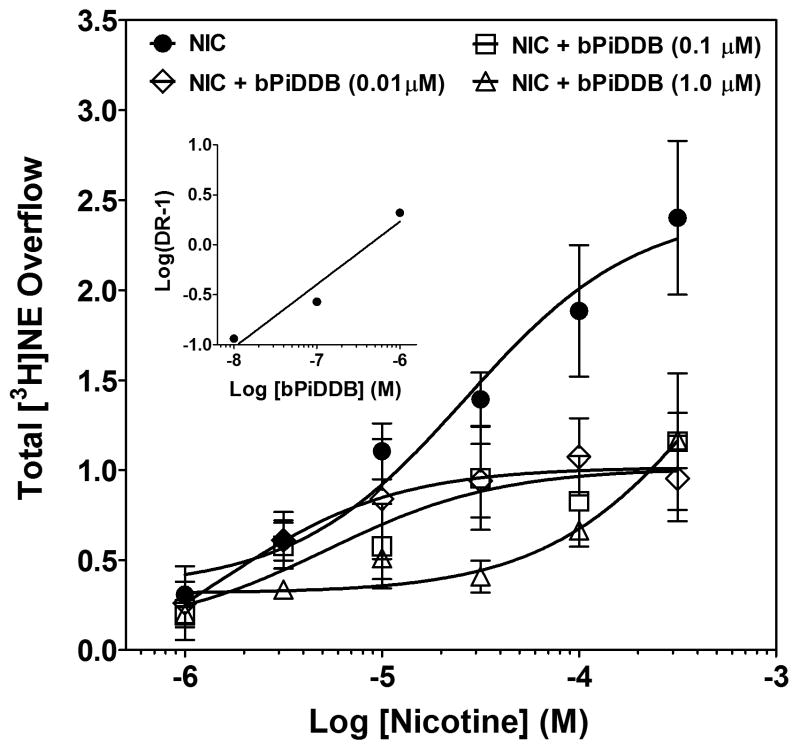
Fig. 7. Schild analysis for bPiDDB inhibition of nicotine-evoked [3H]NE overflow from superfused rat hippocampal slices.
After collection of the third basal sample, slices were superfused with buffer in the absence and presence of bPiDDB (0.01-1.0 μM; between-groups factor) for 30 min before the addition of nicotine (1 – 300 μM; within subjects factor) to the buffer, and superfusion continued for an additional 30 min. Control is the concentration-response for nicotine in the absence of bPiDDB, and the nicotine concentration response was determined contemporaneously for each concentration of bPiDDB. Concentration-response curves were generated using nonlinear regression. Data are presented as mean ± S.E.M. total [3H]NE overflow during the 30-min exposure to nicotine in the absence or presence of mecamylamine; n = 5-7 rats/bPiDDB concentration; control, n = 12 rats. Inset shows the Schild regression in which the log of dr – 1 was plotted as a function of log of bPiDDB concentration and data were fit by linear regression.