FIG. 4.
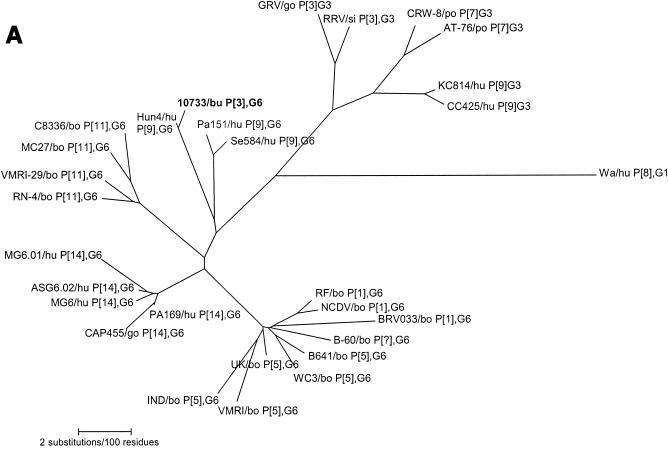
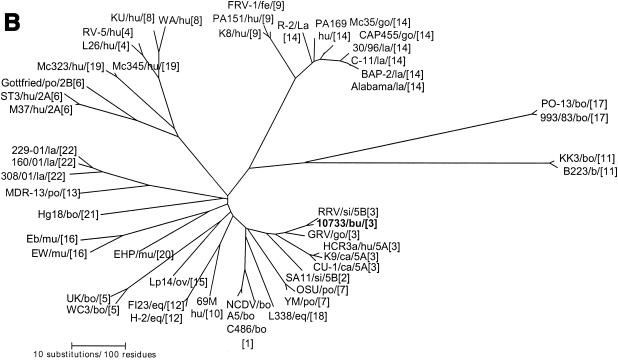
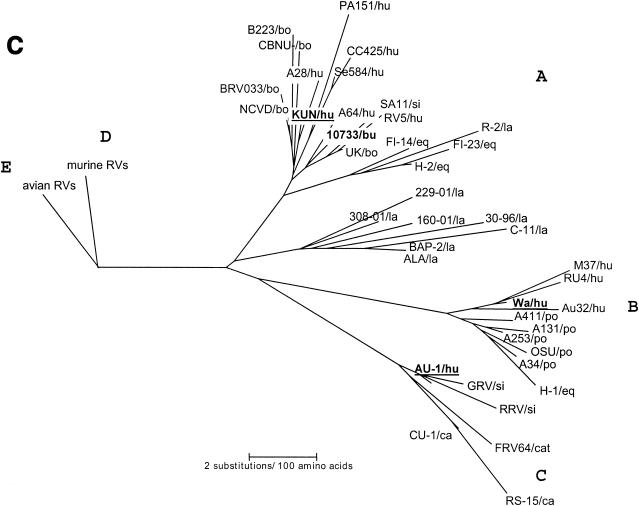
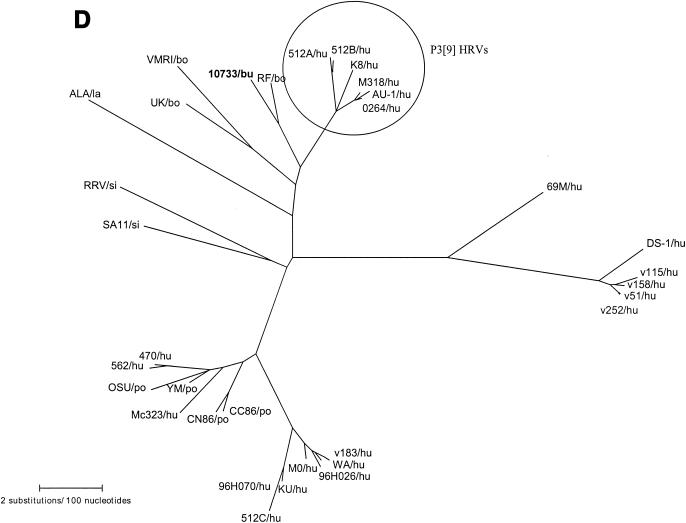
Phylogenetic trees of the VP7, VP8*, and NSP4 amino acid sequences of Italian buffalo strain 10733. (A) VP7 tree, displaying the relationships among a selection of serotype G6 and G3 animal and human rotavirus strains. The dendrogram is drawn to scale and rooted with the human strain Wa (P1A[8],G1). (B) VP8* tree, displaying the relationships among strains representative of all the VP4 genotypes recognized to date. The dendrogram is drawn to scale and rooted with the avian-like bovine strain Bo/993/83 (P[17],G7). (C) NSP4 tree, displaying the relationships among a selection of animal and human rotavirus strains representative of the five NSP4 genetic groups. The branches of the murine (genogroup D) and avian (genogroup E) strains are not to scale. The prototypes of the NSP4 genotypes A, B, and C (strains KUN, Wa, and Au-1, respectively) are boldfaced and underlined. Buffalo 10733 strain is shown in boldface type. (D) NSP5 tree, displaying the relationships among animal and human rotavirus strains. The tree is unrooted and is inferred from the nucleotide alignment. The P3[9] human rotaviruses (HRVs) are enclosed in a circle. Abbreviations: bo, bovine; bu, buffalo; ca, canine; eq, equine; fe, feline; go, goat; hu, human; la, lapine; mu, murine; po, porcine; si, simian.