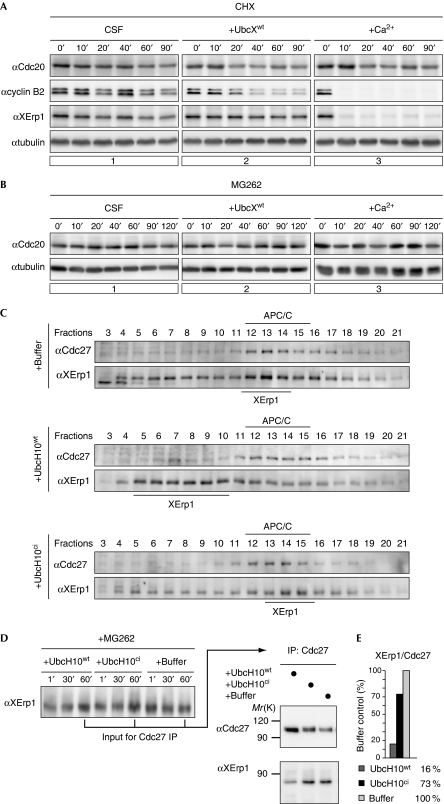
Figure 3.
Cell division cycle 20 is stable in cytostatic factor arrest and UbcH10wt causes the dissociation of the anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome–XErp1 complex. (A) CSF extract treated with CHX was supplemented with buffer control, UbcXwt or calcium. Samples were taken at the indicated time points, treated with phosphatase and analysed by WB for Cdc20, XErp1, cyclin B2 and α-tubulin. (B) CSF extract treated with MG262 was supplemented with buffer control, UbcXwt, or calcium and samples were taken. After phosphatase treatment, Cdc20 and tubulin were analysed by WB. (C) CSF extracts were incubated with buffer, UbcH10wt or UbcH10ci and centrifuged through glycerol gradients. Fractions were taken from high (fraction 3) to low (fraction 21) glycerol concentrations. Cdc27 and XErp1 were detected by WB. (D) CSF extracts containing MG262 were treated as described in (C) and Cdc27 was immunoprecipitated. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to CIP phosphatase treatment and Cdc27 and XErp1 were detected by WB analysis. (E) Quantification of (D). The integrated intensities of Cdc27 and XErp1 signals were measured and the ratio of the signals of XErp1 to Cdc27 was calculated. Buffer control was arbitrarily set to 100. APC/C, anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome; Cdc, cell division cycle; CHX, cycloheximide; ci, catalytically inactive; CIP, calf intestinal alkaline phosphatase; CSF, cytostatic factor; IP, immunoprecipitation; WB, western blotting; wt, wild type.